Facebook Advertisements for Inexpensive Participant Recruitment Among Women in Early Pregnancy
- PMID: 24082026
- PMCID: PMC3976452
- DOI: 10.1177/1090198113504414
Facebook Advertisements for Inexpensive Participant Recruitment Among Women in Early Pregnancy
Abstract
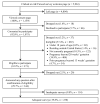
Facebook advertisements were used to recruit nulliparous women in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy for an online survey about their childbirth preferences. A campaign of ads was targeted to women, aged 18 to 44 years, residing in the United States. The ads were viewed 10,577,381 times by 7,248,985 unique Facebook users over 18 weeks in 2011. The ad campaign yielded 6,094 clicks by 5,963 unique users at a mean cost of $0.63 per click and a unique click-through rate of 0.08%. Of those who clicked through to the study site, 18% (n = 1,075) consented to participate. The participant pool was reduced to 344 women after application of strict eligibility criteria. Participants represented 43 states and the District of Columbia, their mean age was 20.9 years (Mdn = 19.0, SD = 4.0), and their mean weeks' gestation was 11.5 (SD = 5.8). The campaign cost was $3,821.81 or $11.11 per eligible participant.
Keywords: maternal and child health; media; quantitative methods; recruitment social media; research design; research subject.
© 2013 Society for Public Health Education.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond Traditional Newspaper Advertisement: Leveraging Facebook-Targeted Advertisement to Recruit Long-Term Smokers for Research.J Med Internet Res. 2016 Jun 15;18(6):e117. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5502. J Med Internet Res. 2016. PMID: 27306780 Free PMC article.
-
Cost and Effectiveness of Using Facebook Advertising to Recruit Young Women for Research: PREFER (Contraceptive Preferences Study) Experience.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Nov 29;21(11):e15869. doi: 10.2196/15869. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31782738 Free PMC article.
-
Broad reach and targeted recruitment using Facebook for an online survey of young adult substance use.J Med Internet Res. 2012 Feb 23;14(1):e28. doi: 10.2196/jmir.1878. J Med Internet Res. 2012. PMID: 22360969 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Cost of Using Facebook Recruitment to Elicit Canadian Women's Perspectives on Bone Health and Osteoporosis: Cross-Sectional Survey Study.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Sep 29;25:e47970. doi: 10.2196/47970. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37773625 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Baseline Assessment Modality on Enrollment and Retention in a Facebook Smoking Cessation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2015 Jul 16;17(7):e179. doi: 10.2196/jmir.4341. J Med Internet Res. 2015. PMID: 26183789 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tweeting it off: characteristics of adults who tweet about a weight loss attempt.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2014 Nov-Dec;21(6):1032-7. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2014-002652. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24928175 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Facebook in Recruiting Participants for Health Research Purposes: A Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2017 Aug 28;19(8):e290. doi: 10.2196/jmir.7071. J Med Internet Res. 2017. PMID: 28851679 Free PMC article.
-
Recruiting young women of color into a pilot RCT targeting sexual health: Lessons learned and implications for applied health technology research.J Am Coll Health. 2022 Jan;70(1):305-313. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2020.1746663. Epub 2020 Apr 28. J Am Coll Health. 2022. PMID: 32343193 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for employing intersectionality in qualitative health research.Soc Sci Med. 2020 Aug;258:113138. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113138. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Soc Sci Med. 2020. PMID: 32574889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripartum women's perspectives on research study participation in the OneFlorida Clinical Research Consortium during COVID-19 pandemic.J Clin Transl Sci. 2022 Oct 10;7(1):e24. doi: 10.1017/cts.2022.476. eCollection 2023. J Clin Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36755549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arcia A. US Nulliparas’ perceptions of roles and of the birth experience as predictors of their childbirth preferences. Midwifery. 2013;29:885–894. doi:10.106/j.midw.2012.10.002. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed B, Jacob P, Allen F, Benowitz N. Attitudes and practices of hookah smokers in the San Francisco Bay Area. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 2011;43(2):146–152. doi:10.1080/02791072.2011.587707. - PubMed
-
- Battistella E, Kalyan S, Prior JC. Evaluation methods and costs associated with recruiting healthy women volunteers to a study of ovulation. Journal of Women’s Health. 2010;19(8):1519–1524. doi:10.1089/jwh.2009.1751. - PubMed
-
- Campaign Cost and Budgeting 2012 Retrieved from: http://www.facebook.com/help/?page=864.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical