Ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest due to 5-fluorouracil cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 24082383
- PMCID: PMC3783134
Ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest due to 5-fluorouracil cardiotoxicity
Abstract
The antimetabolite chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil is used to treat a variety of cancers. Although 5-fluorouracil is generally well tolerated, its toxicity profile includes potential cardiac ischemia, vasospasm, arrhythmia, and direct myocardial injury. These actual or potential toxicities are thought to resolve upon cessation of the medication; however, information about the long-term cardiovascular effects of therapy is not sufficient. We present the case of a 58-year-old man who had 2 ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrests, with evidence of coronary vasospasm and myocarditis, on his 4th day of continuous infusion with 5-fluorouracil. External defibrillation and cessation of the 5-fluorouracil therapy resolved the patient's electrocardiographic abnormalities. In addition to reporting the clinical manifestations of 5-fluorouracil-associated cardiotoxicity in our patient, we discuss management challenges in patients who develop severe 5-fluorouracil-induced ventricular arrhythmias.
Keywords: Arrhythmias, cardiac/chemically induced; coronary vasospasm/chemically induced; fluorouracil/adverse effects; heart diseases/drug therapy; heart/drug effects; myocarditis/chemically induced; treatment outcome.
Figures
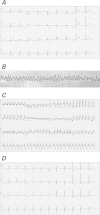

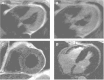
References
-
- Dalzell JR, Samuel LM. The spectrum of 5-fluorouracil cardiotoxicity. Anticancer Drugs 2009;20(1):79–80. - PubMed
-
- Dent RG, McColl I. Letter: 5-Fluorouracil and angina. Lancet 1975;1(7902):347–8. - PubMed
-
- Tsibiribi P, Descotes J, Lombard-Bohas C, Barel C, Bui-Xuan B, Belkhiria M, et al. Cardiotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil in 1350 patients with no prior history of heart disease. Bull Cancer 2006;93(3):E27–30. - PubMed
-
- Stewart T, Pavlakis N, Ward M. Cardiotoxicity with 5-fluorouracil and capecitabine: more than just vasospastic angina. Intern Med J 2010;40(4):303–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
