In vitro antioxidant and H(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibition activities of Acalypha wilkesiana foliage extract
- PMID: 24082698
- PMCID: PMC3778591
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-7406.116822
In vitro antioxidant and H(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibition activities of Acalypha wilkesiana foliage extract
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant activty and anti-acid property of Acalypha wilkesiana foliage extract.
Materials and methods: Hot and cold aqueous extracts were prepared from healthy leaves of A. wilkesiana. Free radical scavenging activity and H(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibition activities of aqueous foliage extracts was screened by in vitro models.
Statistical analysis used: All experiments were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as mean ± SEM.
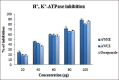
Results: A. wilkesiana hot aqueous extract (AWHE) showed significant antioxidants and free radical scavenging activity. Further, AWHE has shown a potent H(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibitory activity (IC50: 51.5 ± 0.28 μg/ml) when compare to standard proton pump inhibitor omeprazole (56.2 ± 0.64 μg/ml); however, latter activity is equal to A. wilkesiana cold aqueous extract (AWCE). Quantitative analysis of AWHE has revealed more content of phenols and flavonoids; this is found to be the reason for good antioxidant activity over AWCE. Molecular docking was carried out against H(+), K(+)-ATPase enzyme crystal structure to validate the anti-acid activity of A. wilkesiana major phytochemicals.
Conclusions: The present study indicates that the constituents of AWHE and AWCE have good antacid and free radical scavenging activity.
Keywords: Acalypha wilkesiana; Anti-acid; antioxidant; gallic acid; gastric ulcer; molecular docking; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Miller TA. Mechanisms of stress-related mucosal damage. Am J Med. 1987;83:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Ernst PB, Gold BD. The disease spectrum of Helicobacter pylori: The immunopathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000;54:615–40. - PubMed
-
- Langman MJ, Brooks P, Hawkey CJ, Silverstein F, Yeomans N. Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug associated ulcer: Epidemiology, causation and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991;6:442–9. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay U, Biswas K, Chatterjee R, Bandyopadhyay D, Chattopadhyay I, Ganguly CK, et al. Gastroprotective effect of Neem (Azadirachta indica) bark extract: Possible involvement of H(+)-K(+)-ATPase inhibition and scavenging of hydroxyl radical. Life Sci. 2002;71:2845–65. - PubMed
-
- Madanick RD. Proton pump inhibitor side effects and drug interactions: Much ado about nothing? Cleve Clin J Med. 2011;78:39–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

