Epidemiology of animal bite in Aq Qala city, northen of Iran
- PMID: 24083263
- PMCID: PMC3778582
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9531.112682
Epidemiology of animal bite in Aq Qala city, northen of Iran
Abstract
Background: Animal bite is one of the problems of public health which has the potential risk of rabies disease. This study was conducted to determine the epidemiology of animal bite in Aq Qala city from 2000 to 2009.
Materials and methods: In this descriptive cross-sectional study, 13142 cases of animal bites which were recorded in Rabies Treatment Center of Aq Qala City were entered into the study by census method. The data were collected from the registered office profile of people who had referred to this center. The obtained data were analyzed using descriptive statistics (frequency distribution, percentage, mean, and standard deviation) and Chi-square test.
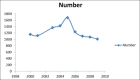
Findings: Of 13142 registered cases, 72.1% were men and 27.9% were women. The mean age of the victims was 25.0 ± 17.8 years, most of whom (84%) lived in villages. Also, most cases of animal bite were done by dogs, (97.8%) occurred in legs (69.6%). Most of the victims were students (28.9%). The highest frequency of bites happened in spring (28.8%). The incidence rate of animal bite was 1222/100,000 people. The highest and lowest incidence rates were 1608/100 000 in 2004 and 1117/100,000 in 2009, respectively. There was a significant relationship between season and the number of bites (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The incidence of animal bite in Aq Qala city was higher than that in other studies in different parts of the country. Considering the high cost of antirabies serum and vaccination, it is essential to take necessary measures reduce the incidence of this problem.
Keywords: Animal bite; Aq Qala; epidemiology; incidence; rabies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiological characteristics and surveillance of animal bite injuries, in Kerman city, Iran.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Aug 29;13:299. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_631_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39416980 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of animal bite in Iran during a 20-year period (1993-2013): a meta-analysis.Trop Med Health. 2019 Nov 29;47:55. doi: 10.1186/s41182-019-0182-5. eCollection 2019. Trop Med Health. 2019. PMID: 31798312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Influencing Animal Bites in Iran: A Descriptive Study.Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016 Aug;7(4):273-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrp.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016. PMID: 27635378 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological study on animal bite cases referred to Haji Daii health Center in Kermanshah province, Iran during 2013-2017.BMC Public Health. 2020 Mar 30;20(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08556-1. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32228562 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of animal bite in Iran: A Systematic review and meta-analysis.J Res Med Sci. 2023 Jul 28;28:59. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_190_22. eCollection 2023. J Res Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38024520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological Patterns of Animal Bites in the Najafabad, Center of Iran (2012-2017).Ann Glob Health. 2020 Apr 7;86(1):38. doi: 10.5334/aogh.2776. Ann Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32292711 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of dog bite injuries in patients presenting at Kimberley Hospital Complex's emergency and gateway centres, 2015 to 2017.Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2020 May 21;12(1):e1-e7. doi: 10.4102/phcfm.v12i1.2301. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2020. PMID: 32501026 Free PMC article.
-
Rabies Vaccination and Public Health Insights in the Extended Arabian Gulf and Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Scoping Review.Diseases. 2025 Apr 21;13(4):124. doi: 10.3390/diseases13040124. Diseases. 2025. PMID: 40277834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suspected Rabies in Humans and Animals, Laikipia County, Kenya.Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 Mar;22(3):551-3. doi: 10.3201/eid2203.151118. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26890989 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Epidemiological Study of Animal Bites and Rabies in Lorestan Province in West of Iran During 2004-2014 for Preventive Purposes.Int J Prev Med. 2016 Sep 8;7:104. doi: 10.4103/2008-7802.190090. eCollection 2016. Int J Prev Med. 2016. PMID: 27688868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dadipour M, Salahi R, Ghezelsofla F. Animal bite epidemiology of stigma in the city during 2003-2005. J Gorgan Uni Med Sci. 2009;11:76–9.
-
- 1st ed. Tehran: Pasteur Institute of Iran and Center for Disease Management; 2003. National Guid lines for Rabies Control; pp. 5–6.
-
- World organization for Animal Health. Rabies: A priority for human and animal, Bulletin. 2011;3:11.
-
- WHO. Eastern Mediterranean Region Annual ports of Regional Director (1950-2000), Alexandria World Health Organization Regional office for Eastern Mediterranean Region. 2000
-
- Geneva, Switzerland: 2001. WHO. Strategies for the control and elimination of rabies in Asia, Report of a WHO Interregional Consultation.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources