Variant callers for next-generation sequencing data: a comparison study
- PMID: 24086590
- PMCID: PMC3785481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075619
Variant callers for next-generation sequencing data: a comparison study
Abstract
Next generation sequencing (NGS) has been leading the genetic study of human disease into an era of unprecedented productivity. Many bioinformatics pipelines have been developed to call variants from NGS data. The performance of these pipelines depends crucially on the variant caller used and on the calling strategies implemented. We studied the performance of four prevailing callers, SAMtools, GATK, glftools and Atlas2, using single-sample and multiple-sample variant-calling strategies. Using the same aligner, BWA, we built four single-sample and three multiple-sample calling pipelines and applied the pipelines to whole exome sequencing data taken from 20 individuals. We obtained genotypes generated by Illumina Infinium HumanExome v1.1 Beadchip for validation analysis and then used Sanger sequencing as a "gold-standard" method to resolve discrepancies for selected regions of high discordance. Finally, we compared the sensitivity of three of the single-sample calling pipelines using known simulated whole genome sequence data as a gold standard. Overall, for single-sample calling, the called variants were highly consistent across callers and the pairwise overlapping rate was about 0.9. Compared with other callers, GATK had the highest rediscovery rate (0.9969) and specificity (0.99996), and the Ti/Tv ratio out of GATK was closest to the expected value of 3.02. Multiple-sample calling increased the sensitivity. Results from the simulated data suggested that GATK outperformed SAMtools and glfSingle in sensitivity, especially for low coverage data. Further, for the selected discrepant regions evaluated by Sanger sequencing, variant genotypes called by exome sequencing versus the exome array were more accurate, although the average variant sensitivity and overall genotype consistency rate were as high as 95.87% and 99.82%, respectively. In conclusion, GATK showed several advantages over other variant callers for general purpose NGS analyses. The GATK pipelines we developed perform very well.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
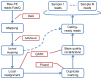



References
-
- Nielsen R, Paul JS, Albrechtsen A, Song YS (2011) Genotype and SNP calling from next-generation sequencing data. Nat Rev Genet 12: 443-451. doi:10.1038/nrg2986. PubMed: 21587300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruffalo M, LaFramboise T, Koyutürk M (2011) Comparative analysis of algorithms for next-generation sequencing read alignment. Bioinformatics 27: 2790-2796. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr477. PubMed: 21856737. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pattnaik S, Vaidyanathan S, Pooja DG, Deepak S, Panda B (2012) Customisation of the Exome Data Analysis Pipeline Using a Combinatorial Approach. PLOS ONE 7: e30080. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030080. PubMed: 22238694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25: 1754-1760. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. PubMed: 19451168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Jiang R, Kwan W, Wang B, Ma X et al. (2011) Evaluation of next-generation sequencing software in mapping and assembly. J Hum Genet 56: 406-414. doi:10.1038/jhg.2011.43. PubMed: 21525877. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RC2 DA028909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA18432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024138/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH064122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA028909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA030976/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA24758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA024758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030976/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA017535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH64122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

