Tamoxifen inhibition of kv7.2/kv7.3 channels
- PMID: 24086693
- PMCID: PMC3782443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076085
Tamoxifen inhibition of kv7.2/kv7.3 channels
Abstract
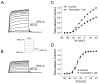
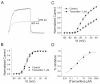
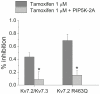
KCNQ genes encode five Kv7 K(+) channel subunits (Kv7.1-Kv7.5). Four of these (Kv7.2-Kv7.5) are expressed in the nervous system. Kv7.2 and Kv7.3 are the principal molecular components of the slow voltage-gated M-channel, which regulates neuronal excitability. In this study, we demonstrate that tamoxifen, an estrogen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of breast cancer, inhibits Kv7.2/Kv7.3 currents heterologously expressed in human embryonic kidney HEK-293 cells. Current inhibition by tamoxifen was voltage independent but concentration-dependent. The IC50 for current inhibition was 1.68 ± 0.44 µM. The voltage-dependent activation of the channel was not modified. Tamoxifen inhibited Kv7.2 homomeric channels with a higher potency (IC50 = 0.74 ± 0.16 µM). The mutation Kv7.2 R463E increases phosphatidylinositol- 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) - channel interaction and diminished dramatically the inhibitory effect of tamoxifen compared with that for wild type Kv7.2. Conversely, the mutation Kv7.2 R463Q, which decreases PIP2 -channel interaction, increased tamoxifen potency. Similar results were obtained on the heteromeric Kv7.2 R463Q/Kv7.3 and Kv7.2 R463E/Kv7.3 channels, compared to Kv7.2/Kv7.3 WT. Overexpression of type 2A PI(4)P5-kinase (PIP5K 2A) significantly reduced tamoxifen inhibition of Kv7.2/Kv7.3 and Kv7.2 R463Q channels. Our results suggest that tamoxifen inhibited Kv7.2/Kv7.3 channels by interfering with PIP2-channel interaction because of its documented interaction with PIP2 and the similar effect of tamoxifen on various PIP2 sensitive channels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Jentsch TJ (2000) Neuronal KCNQ potassium channels: physiology and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 1: 21-30. doi:10.1038/35036198. PubMed: 11252765. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang HS, Pan Z, Shi W, Brown BS, Wymore RS et al. (1998) KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: molecular correlates of the M-channel. Science 282: 1890-1893. doi:10.1126/science.282.5395.1890. PubMed: 9836639. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Adams PR (1980) Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature 283: 673-676. doi:10.1038/283673a0. PubMed: 6965523. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delmas P, Brown DA (2005) Pathways modulating neural KCNQ/M (Kv7) potassium channels. Nat Rev Neurosci 6: 850-862. doi:10.1038/nrm1746. PubMed: 16261179. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marrion NV (1997) Control of M-current. Annu Rev Physiol 59: 483-504. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.59.1.483. PubMed: 9074774. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

