New generation of ensemble-decision aliquot ranking based on simplified microfluidic components for large-capacity trapping of circulating tumor cells
- PMID: 24087951
- PMCID: PMC3839942
- DOI: 10.1021/ac401985r
New generation of ensemble-decision aliquot ranking based on simplified microfluidic components for large-capacity trapping of circulating tumor cells
Abstract
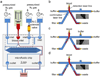
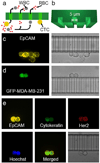
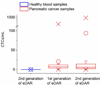
Ensemble-decision aliquot ranking (eDAR) is a sensitive and high-throughput method to analyze circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from peripheral blood. Here, we report the next generation of eDAR, where we designed and optimized a new hydrodynamic switching scheme for the active sorting step in eDAR, which provided fast cell sorting with an improved reproducibility and stability. The microfluidic chip was also simplified by incorporating a functional area for subsequent purification using microslits fabricated by standard lithography method. Using the reported second generation of eDAR, we were able to analyze 1 mL of whole-blood samples in 12.5 min, with a 95% recovery and a zero false positive rate (n = 15).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.T.C. and P.G.S. have financial interest in MiCareo, which has licensed the described technology from the University of Washington.
Figures
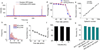
References
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. Science. 2011;331:1559–1564. - PubMed
-
- Mocellin S, Keilholz U, Rossi CR, Nitti D. Trends Mol. Med. 2006;12:130–139. - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Alix-Panabieres C, Riethdorf S. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009;6:339–351. - PubMed
-
- Paterlini-Brechot P, Benali NL. Cancer Lett. 2007;253:180–204. - PubMed
-
- Andreopoulou E, Cristofanilli M. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010;10:171–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

