Multifunctional nanorods serving as nanobridges to modulate T cell-mediated immunity
- PMID: 24088178
- PMCID: PMC3972813
- DOI: 10.1021/nn403275p
Multifunctional nanorods serving as nanobridges to modulate T cell-mediated immunity
Abstract
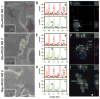
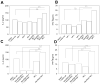
Electrodeposited nanorods serving as multivalent bridges were fabricated and surface-decorated with ligands for immune cells. Gold and nickel solutions were sequentially electrodeposited on nanoporous anodized disc templates and the template was dissolved to retrieve bisegmented nanorods with different lengths. Gold and nickel segmented nanorods were surface-immobilized with mannose and RGD peptides to prepare immune-cell recruiting nanorods. Surface-functionalization of nanorods were confirmed by fluorescence-labeling of each ligands and confocal microscopy. Dendritic cells and T cells were co-incubated with the surface-functionalized nanorods, and the proximity between the nanorods and the immune cells was visualized by variable pressure scanning electron microscopy and confocal microscopy. The long nanorods were associated with the immune cells, whereas the shorter nanorods were rather endocytosed by cells, suggesting a feasibility of the longer nanorods as bridging for the cells. Cytokine releases from the immune cells were monitored by cultivating lipopolysaccharide-activated dendritic cells with T cells. Interleukine-2 and interferon-γ release profiles showed a strong correlation with the length of the nanorod, where the 4 μm nanorods induced the highest levels of cytokine release compared to 1 or 2 μm nanorods. Thus, we concluded that the proximity of the immune cells increased by bridging the immune cells with the nanobridging system, which subsequently increased cytokine release by facilitating the antigen presentation process.
Figures


References
-
- Kalishwaralal K, Banumathi E, Ram Kumar Pandian S, Deepak V, Muniyandi J, Eom SH, Gurunathan S. Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit Vegf Induced Cell Proliferation and Migration in Bovine Retinal Endothelial Cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;73:51–7. - PubMed
-
- Krippner-Heidenreich A, Tubing F, Bryde S, Willi S, Zimmermann G, Scheurich P. Control of Receptor-Induced Signaling Complex Formation by the Kinetics of Ligand/Receptor Interaction. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44155–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

