Short tandem repeats in the inhibitory domain of the mineralocorticoid receptor: prediction of a β-solenoid structure
- PMID: 24088384
- PMCID: PMC3851330
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-13-17
Short tandem repeats in the inhibitory domain of the mineralocorticoid receptor: prediction of a β-solenoid structure
Abstract
Background: The human mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) is one of the main components of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), the system that regulates the body exchange of water and sodium. The evolutionary origins of this protein predate those of renin and the RAAS; accordingly it has other roles, which are being characterized. The MR has two trans-activating ligand independent domains and one inhibitory domain (ID), which modulates the activity of the former. The structure of the ID is currently unknown.
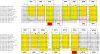
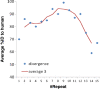
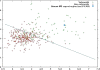
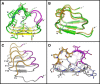
Results: Here we report that the ID contains at least 15 tandem repeats of around 10 amino acids, which we computationally characterize in the human MR and in selected orthologs. This ensemble of repeats seems to have emerged around 450 million years ago, after the divergence of the MR from its close homolog, the glucocorticoid receptor, which does not possess the repeats. The region would have quickly expanded by successive duplication of the repeats stabilizing at its length in human MR shortly after divergence of tetrapoda from bony fishes 400 million years ago. Structural predictions, in combination with molecular dynamics simulations suggest that the repeat ensemble forms a β-solenoid, namely a β-helical fold with a polar core, stabilized by hydrogen-bonded ladders of polar residues. Our 3D-model, in conjunction with previous experimental data, implies a role of the β-helical fold as a scaffold for multiple intra-and inter-molecular interactions and that these interactions are modulated via phosphorylation-dependent conformational changes.
Conclusions: We, thus, propose that the structure of the repeat ensemble plays an important role in the coordination and sequential interactions of various MR partners and therefore in the functionality and specificity of MR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evolution of hormone selectivity in glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;137:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23907018 Review.
-
Conformation of the mineralocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain: evidence for induced and stable structure.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Oct;24(10):1935-48. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0005. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20685853 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biochemical mechanisms for the specificity of hormone binding and coactivator assembly by mineralocorticoid receptor.Mol Cell. 2005 Aug 5;19(3):367-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.026. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16061183
-
Crystal structure of an ancient protein: evolution by conformational epistasis.Science. 2007 Sep 14;317(5844):1544-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1142819. Epub 2007 Aug 16. Science. 2007. PMID: 17702911 Free PMC article.
-
[Corticosteroid hormones: mechanisms involved in the recognition of aldosterone by mineralocorticoid receptors].J Soc Biol. 1999;193(4-5):355-60. J Soc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10689617 Review. French.
Cited by
-
PlaToLoCo: the first web meta-server for visualization and annotation of low complexity regions in proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 2;48(W1):W77-W84. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa339. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32421769 Free PMC article.
-
RepeatsDB 2.0: improved annotation, classification, search and visualization of repeat protein structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D308-D312. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1136. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899671 Free PMC article.
-
Structured Tandem Repeats in Protein Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 5;25(5):2994. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052994. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474241 Free PMC article.
-
Ssn6-Tup1 global transcriptional co-repressor: Role of the N-terminal glutamine-rich region of Ssn6.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 20;12(10):e0186363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186363. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29053708 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal domain of TPX2 is made of alpha-helical tandem repeats.BMC Struct Biol. 2016 Oct 26;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12900-016-0070-8. BMC Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27782824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade MA, Perez-Iratxeta C, Ponting CP. Protein repeats: structures, functions, and evolution. J Struct Biol. 2001;134(2–3):117–131. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

