Linezolid-induced optic neuropathy
- PMID: 24088636
- PMCID: PMC4064234
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.118451
Linezolid-induced optic neuropathy
Abstract
Many systemic antimicrobials have been implicated to cause ocular adverse effects. This is especially relevant in multidrug therapy where more than one drug can cause a similar ocular adverse effect. We describe a case of progressive loss of vision associated with linezolid therapy. A 45-year-old male patient who was on treatment with multiple second-line anti-tuberculous drugs including linezolid and ethambutol for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) presented to us with painless progressive loss of vision in both eyes. Color vision was defective and fundus examination revealed optic disc edema in both eyes. Ethambutol-induced toxic optic neuropathy was suspected and tablet ethambutol was withdrawn. Deterioration of vision occurred despite withdrawal of ethambutol. Discontinuation of linezolid resulted in marked improvement of vision. Our report emphasizes the need for monitoring of visual function in patients on long-term linezolid treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





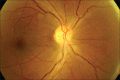
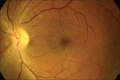



Comment in
-
Comment on Linezolid induced optic neuropathy.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015 Jan;63(1):75-6. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.151484. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25686072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- De Vriese AS, Coster RV, Smet J, Seneca S, Lovering A, Van Haute LL, et al. Linezolid-induced inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:1111–7. - PubMed
-
- Narita M, Tsuji BT, Yu VL. Linezolid- associated peripheral and optic neuropathy, lactic acidosis and serotonin syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 2007;27:1189–97. - PubMed
-
- Rydalmere, NSW: Pharmacia Australia; 2002. Zyvox (linezolid) product information.
-
- Azamfirei L, Copotoiu SM, Branzaniuc K, Szederjesi J, Copotoiu R, Berteanu C. Complete blindness after optic neuropathy induced by short-term linezolid treatment in a patient suffering from muscle dystrophy. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2007;16:402–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

