Hyperperfusion in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is associated with disease progression and absence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
- PMID: 24088807
- PMCID: PMC3808691
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awt268
Hyperperfusion in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is associated with disease progression and absence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
Abstract
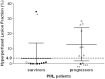
We sought to characterize perfusion patterns of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions by arterial spin labelling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging and to analyse their association with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome, and survival. A total of 22 patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy underwent a clinical evaluation and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain within 190 days of symptom onset. The presence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome was determined based on clinical and laboratory criteria. Perfusion within progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions was determined by arterial spin labelling magnetic resonance imaging. We observed intense hyperperfusion within and at the edge of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions in a subset of subjects. This hyperperfusion was quantified by measuring the fraction of lesion volume showing perfusion in excess of twice normal appearing grey matter. Hyperperfused lesion fraction was significantly greater in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy progressors than in survivors (12.8% versus 3.4% P = 0.02) corresponding to a relative risk of progression for individuals with a hyperperfused lesion fraction ≥ 4.0% of 9.1 (95% confidence interval of 1.4-59.5). The presence of hyperperfusion was inversely related to the occurrence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome at the time of scan (P = 0.03). Indeed, within 3 months after symptom onset, hyperperfusion had a positive predictive value of 88% for absence of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Arterial spin labelling magnetic resonance imaging recognized regions of elevated perfusion within lesions of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. These regions might represent virologically active areas operating in the absence of an effective adaptive immune response and correspond with a worse prognosis.
Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimmunology; neuroinflammation; perfusion imaging; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Abrams J. Nitrate delivery systems in perspective. A decade of progress. Am J Med. 1984;76:38–46. - PubMed
-
- Aiello S, Noris M, Piccinini G, Tomasoni S, Casiraghi F, Bonazzola S, et al. Thymic dendritic cells express inducible nitric oxide synthase and generate nitric oxide in response to self- and alloantigens. J Immunol. 2000;164:4649–58. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Reduced transit-time sensitivity in noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of human cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:1236–49. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA, Grossman M. Assessment of cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer's disease by spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

