Comparison of multiple red cell volume methods performed concurrently in premature infants following allogeneic transfusion
- PMID: 24088873
- PMCID: PMC3907947
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2013.143
Comparison of multiple red cell volume methods performed concurrently in premature infants following allogeneic transfusion
Abstract
Background: Study of the pathophysiology and treatment of anemia of prematurity is facilitated by direct measurement of red cell volume (RCV) utilizing microliter quantities of blood samples. Our objective was to compare concurrent measurements of multiple direct RCV methods in infants.
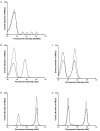
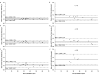
Methods: Eighteen preterm infants receiving clinically indicated transfusions had concurrent flow cytometric determinations of RCV and 24-h red blood cell (RBC) recovery based on donor-recipient differences of biotin-labeled RBCs (BioRBCs), Kidd antigen mismatched RBCs, and fetal hemoglobin-positive (HbF(+)) RBCs. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was also used for measuring HbF and adult hemoglobin protein concentrations for the determination of RCV.
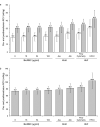
Results: Concurrent RCV measurements using BioRBCs (18 and 54 µg/ml), Kidd antigen, and HbF flow cytometry were not statistically different compared with RCVs measured using the reference BioRBC density (6 µg/ml). By contrast, the HbF-HPLC method overestimated RCV by 45% compared with the reference method. All the methods demonstrated 100% 24-h posttransfusion RBC recovery (PTR24).
Conclusion: Because BioRBC, Kidd antigen, and fetal hemoglobin (HbF) flow cytometry are safe and accurate methods requiring <10 µl of patient blood for determining RCV and PTR24 in preterm infants, they can be useful in clinical and research studies of anemia and other conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Jones JG, Holland BM, Hudson IR, Wardrop CA. Total circulating red cells versus haematocrit as the primary descriptor of oxygen transport by the blood. Br J Haematol. 1990;76:288–94. - PubMed
-
- Mock DM, Bell EF, Lankford GL, Widness JA. Hematocrit correlates well with circulating red blood cell volume in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 2001;50:525–31. - PubMed
-
- Davis BH, Olsen S, Bigelow NC, Chen JC. Detection of fetal red cells in fetomaternal hemorrhage using a fetal hemoglobin monoclonal antibody by flow cytometry. Transfusion. 1998;38:749–56. - PubMed
-
- Dziegiel MH, Nielsen LK, Berkowicz A. Detecting fetomaternal hemorrhage by flow cytometry. Curr Opin Hematol. 2006;13:490–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

