Highly sensitive real-time in vivo imaging of an influenza reporter virus reveals dynamics of replication and spread
- PMID: 24089552
- PMCID: PMC3838222
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02381-13
Highly sensitive real-time in vivo imaging of an influenza reporter virus reveals dynamics of replication and spread
Abstract
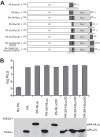
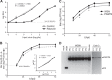
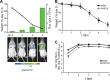
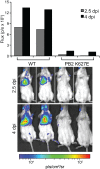
The continual public health threat posed by the emergence of novel influenza viruses necessitates the ability to rapidly monitor infection and spread in experimental systems. To analyze real-time infection dynamics, we have created a replication-competent influenza reporter virus suitable for in vivo imaging. The reporter virus encodes the small and bright NanoLuc luciferase whose activity serves as an extremely sensitive readout of viral infection. This virus stably maintains the reporter construct and replicates in culture and in mice with near-native properties. Bioluminescent imaging of the reporter virus permits serial observations of viral load and dissemination in infected animals, even following clearance of a sublethal challenge. We further show that the reporter virus recapitulates known restrictions due to host range and antiviral treatment, suggesting that this technology can be applied to studying emerging influenza viruses and the impact of antiviral interventions on infections in vivo. These results describe a generalizable method to quickly determine the replication and pathogenicity potential of diverse influenza strains in animals.
Figures
References
-
- WHO 2009. 2009 Influenza (seasonal) fact sheet. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/
-
- Thompson MG, Shay DK, Zhou H, Bridges CB, Cheng PY, Burns E, Bresee JS, Cox NJ. 2010. Estimates of deaths associated with seasonal influenza—United States, 1976–2007. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 59:1057–1062 - PubMed
-
- Gao R, Cao B, Hu Y, Feng Z, Wang D, Hu W, Chen J, Jie Z, Qiu H, Xu K, Xu X, Lu H, Zhu W, Gao Z, Xiang N, Shen Y, He Z, Gu Y, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Zhao X, Zhou L, Li X, Zou S, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang L, Guo J, Dong J, Li Q, Dong L, Zhu Y, Bai T, Wang S, Hao P, Yang W, Zhang Y, Han J, Yu H, Li D, Gao GF, Wu G, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Shu Y. 2013. Human infection with a novel avian-origin influenza A (H7N9) virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 368:1888–1897 - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Zhou L, Zhou M, Chen Z, Li F, Wu H, Xiang N, Chen E, Tang F, Wang D, Meng L, Hong Z, Tu W, Cao Y, Li L, Ding F, Liu B, Wang M, Xie R, Gao R, Li X, Bai T, Zou S, He J, Hu J, Xu Y, Chai C, Wang S, Gao Y, Jin L, Zhang Y, Luo H, Yu H, Gao L, Pang X, Liu G, Shu Y, Yang W, Uyeki TM, Wang Y, Wu F, Feng Z. 24 April 2013. Preliminary report: epidemiology of the avian influenza A (H7N9) outbreak in China. N. Engl. J. Med. [Epub ahead of print.] 10.1056/NEJMoa1304617 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

