Mutations in the parainfluenza virus 5 fusion protein reveal domains important for fusion triggering and metastability
- PMID: 24089572
- PMCID: PMC3838234
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02123-13
Mutations in the parainfluenza virus 5 fusion protein reveal domains important for fusion triggering and metastability
Abstract
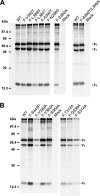
Paramyxovirus membrane glycoproteins F (fusion protein) and HN, H, or G (attachment protein) are critical for virus entry, which occurs through fusion of viral and cellular envelopes. The F protein folds into a homotrimeric, metastable prefusion form that can be triggered by the attachment protein to undergo a series of structural rearrangements, ultimately folding into a stable postfusion form. In paramyxovirus-infected cells, the F protein is activated in the Golgi apparatus by cleavage adjacent to a hydrophobic fusion peptide that inserts into the target membrane, eventually bringing the membranes together by F refolding. However, it is not clear how the attachment protein, known as HN in parainfluenza virus 5 (PIV5), interacts with F and triggers F to initiate fusion. To understand the roles of various F protein domains in fusion triggering and metastability, single point mutations were introduced into the PIV5 F protein. By extensive study of F protein cleavage activation, surface expression, and energetics of fusion triggering, we found a role for an immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domain, where multiple hydrophobic residues on the PIV5 F protein may mediate F-HN interactions. Additionally, destabilizing mutations of PIV5 F that resulted in HN trigger-independent mutant F proteins were identified in a region along the border of F trimer subunits. The positions of the potential HN-interacting region and the region important for F stability in the lower part of the PIV5 F prefusion structure provide clues to the receptor-binding initiated, HN-mediated F trigger.
Figures




References
-
- Lamb RA. 2007. Mononegavirales, p 1357–1361 In Knipe DM, Howley PM. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
-
- Heminway BR, Yu Y, Galinski MS. 1994. Paramyxovirus mediated cell fusion requires co-expression of both the fusion and hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoproteins. Virus Res. 31:1–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

