Superficial dosimetry imaging based on Čerenkov emission for external beam radiotherapy with megavoltage x-ray beam
- PMID: 24089916
- PMCID: PMC3790817
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4821543
Superficial dosimetry imaging based on Čerenkov emission for external beam radiotherapy with megavoltage x-ray beam
Abstract
Purpose: Čerenkov radiation emission occurs in all tissue, when charged particles (either primary or secondary) travel at velocity above the threshold for the Čerenkov effect (about 220 KeV in tissue for electrons). This study presents the first examination of optical Čerenkov emission as a surrogate for the absorbed superficial dose for MV x-ray beams.
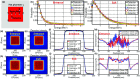
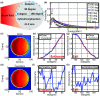
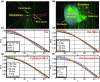
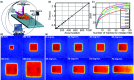
Methods: In this study, Monte Carlo simulations of flat and curved surfaces were studied to analyze the energy spectra of charged particles produced in different regions near the surfaces when irradiated by MV x-ray beams. Čerenkov emission intensity and radiation dose were directly simulated in voxelized flat and cylindrical phantoms. The sampling region of superficial dosimetry based on Čerenkov radiation was simulated in layered skin models. Angular distributions of optical emission from the surfaces were investigated. Tissue mimicking phantoms with flat and curved surfaces were imaged with a time domain gating system. The beam field sizes (50 × 50-200 × 200 mm(2)), incident angles (0°-70°) and imaging regions were all varied.
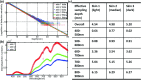
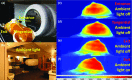
Results: The entrance or exit region of the tissue has nearly homogeneous energy spectra across the beam, such that their Čerenkov emission is proportional to dose. Directly simulated local intensity of Čerenkov and radiation dose in voxelized flat and cylindrical phantoms further validate that this signal is proportional to radiation dose with absolute average discrepancy within 2%, and the largest within 5% typically at the beam edges. The effective sampling depth could be tuned from near 0 up to 6 mm by spectral filtering. The angular profiles near the theoretical Lambertian emission distribution for a perfect diffusive medium, suggesting that angular correction of Čerenkov images may not be required even for curved surface. The acquisition speed and signal to noise ratio of the time domain gating system were investigated for different acquisition procedures, and the results show there is good potential for real-time superficial dose monitoring. Dose imaging under normal ambient room lighting was validated, using gated detection and a breast phantom.
Conclusions: This study indicates that Čerenkov emission imaging might provide a valuable way to superficial dosimetry imaging in real time for external beam radiotherapy with megavoltage x-ray beams.
Figures

References
-
- Habibollahi F., Mayles H. M., Mayles W. P., Winter P. J., Tong D., Fentiman I. S., Chaudary M. A., and Hayward J. L., “Assessment of skin dose and its relation to cosmesis in the conservative treatment of early breast cancer,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. 14, 291–296 (1988). 10.1016/0360-3016(88)90435-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

