p16(INK4a) protects against dysfunctional telomere-induced ATR-dependent DNA damage responses
- PMID: 24091330
- PMCID: PMC3784543
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI69574
p16(INK4a) protects against dysfunctional telomere-induced ATR-dependent DNA damage responses
Abstract
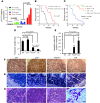
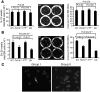
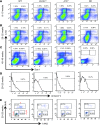
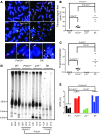
Dysfunctional telomeres limit cellular proliferative capacity by activating the p53-p21- and p16(INK4a)-Rb-dependent DNA damage responses (DDRs). The p16(INK4a) tumor suppressor accumulates in aging tissues, is a biomarker for cellular senescence, and limits stem cell function in vivo. While the activation of a p53-dependent DDR by dysfunctional telomeres has been well documented in human cells and mouse models, the role for p16(INK4a) in response to telomere dysfunction remains unclear. Here, we generated protection of telomeres 1b p16-/- mice (Pot1bΔ/Δ;p16-/-) to address the function of p16(INK4a) in the setting of telomere dysfunction in vivo. We found that deletion of p16(INK4a) accelerated organ impairment and observed functional defects in highly proliferative organs, including the hematopoietic system, small intestine, and testes. Pot1bΔ/Δ;p16-/- hematopoietic cells exhibited increased telomere loss, increased chromosomal fusions, and telomere replication defects. p16(INK4a) deletion enhanced the activation of the ATR-dependent DDR in Pot1bΔ/Δ hematopoietic cells, leading to p53 stabilization, increased p21-dependent cell cycle arrest, and elevated p53-dependent apoptosis. In contrast to p16(INK4a), deletion of p21 did not activate ATR, rescued proliferative defects in Pot1bΔ/Δ hematopoietic cells, and significantly increased organismal lifespan. Our results provide experimental evidence that p16(INK4a) exerts protective functions in proliferative cells bearing dysfunctional telomeres.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significant role for p16INK4a in p53-independent telomere-directed senescence.Curr Biol. 2004 Dec 29;14(24):2302-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.025. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15620660
-
Ink4a/Arf tumor suppressor does not modulate the degenerative conditions or tumor spectrum of the telomerase-deficient mouse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 6;104(10):3931-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700093104. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360455 Free PMC article.
-
p16INK4A enhances the transcriptional and the apoptotic functions of p53 through DNA-dependent interaction.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jul;56(7):1687-1702. doi: 10.1002/mc.22627. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28218424 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology of p16(INK4A)-mediated G1 proliferative arrest.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000;33(2):189-97. doi: 10.1385/CBB:33:2:189. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11325039 Review.
-
Telomere dysfunction and stem cell ageing.Biochimie. 2008 Jan;90(1):24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.09.006. Epub 2007 Sep 22. Biochimie. 2008. PMID: 18029082 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of p16 does not protect against premature ovarian insufficiency caused by alkylating agents.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Mar 8;23(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05476-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 36890528 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Telomere Biology in Cell Senescence, Replicative and Chronological Ageing.Cells. 2019 Jan 15;8(1):54. doi: 10.3390/cells8010054. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30650660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Pathways Control the Reactivation of Telomerase in HTLV-I-Associated Leukemia.Int J Cancer Oncol. 2015 Jun 2;2(2):215. doi: 10.15436/2377-0902.15.017. Int J Cancer Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26430700 Free PMC article.
-
Safeguarding genomic integrity in beta-cells: implications for beta-cell differentiation, growth, and dysfunction.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Oct 30;52(5):2133-2144. doi: 10.1042/BST20231519. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39364746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pot1 OB-fold mutations unleash telomere instability to initiate tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2017 Apr 6;36(14):1939-1951. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.405. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27869160 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

