Micro- and nanoscale devices for the investigation of epigenetics and chromatin dynamics
- PMID: 24091454
- PMCID: PMC4072028
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2013.195
Micro- and nanoscale devices for the investigation of epigenetics and chromatin dynamics
Abstract
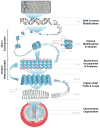
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the blueprint on which life is based and transmitted, but the way in which chromatin - a dynamic complex of nucleic acids and proteins - is packaged and behaves in the cellular nucleus has only begun to be investigated. Epigenetic modifications sit 'on top of' the genome and affect how DNA is compacted into chromatin and transcribed into ribonucleic acid (RNA). The packaging and modifications around the genome have been shown to exert significant influence on cellular behaviour and, in turn, human development and disease. However, conventional techniques for studying epigenetic or conformational modifications of chromosomes have inherent limitations and, therefore, new methods based on micro- and nanoscale devices have been sought. Here, we review the development of these devices and explore their use in the study of DNA modifications, chromatin modifications and higher-order chromatin structures.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Introduction into the analysis of high-throughput-sequencing based epigenome data.Brief Bioinform. 2010 Sep;11(5):512-23. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbq014. Epub 2010 May 10. Brief Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 20457755 Review.
-
Chromatin higher-order structures and gene regulation.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011 Apr;21(2):175-86. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.01.022. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011. PMID: 21342762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Chromatin dynamics: nucleosomes go mobile through twist defects.Phys Rev Lett. 2003 Oct 3;91(14):148103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.148103. Epub 2003 Oct 1. Phys Rev Lett. 2003. PMID: 14611559
-
Molecular structures guide the engineering of chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 27;45(13):7555-7570. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx531. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28609787 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Three-dimensional chromatin re-organization during muscle stem cell aging.Aging Cell. 2023 Apr;22(4):e13789. doi: 10.1111/acel.13789. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 36727578 Free PMC article.
-
On-chip transporting arresting and characterizing individual nano-objects in biological ionic liquids.Sci Adv. 2021 Jul 2;7(27):eabd8758. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd8758. Print 2021 Jul. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34215575 Free PMC article.
-
Lead exposure induces dysregulation of constitutive heterochromatin hallmarks in live cells.Curr Res Toxicol. 2021 Dec 11;3:100061. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2021.12.001. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 35005634 Free PMC article.
-
Internal Motion of Chromatin Fibers Is Governed by Dynamics of Uncompressed Linker Strands.Biophys J. 2020 Dec 1;119(11):2326-2334. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.10.018. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 33121944 Free PMC article.
-
Fast detection, a precise and sensitive diagnostic agent for breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 13;41(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02393-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35698159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bird A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature. 2007;447:396–398. - PubMed
-
- Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nature Biotech. 2010;28:1057–1068. - PubMed
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

