Genetic influences on the development of alcoholism
- PMID: 24091936
- PMCID: PMC4159132
- DOI: 10.1007/s11920-013-0412-1
Genetic influences on the development of alcoholism
Abstract
Alcoholism has a substantial heritability yet the detection of specific genetic influences has largely proved elusive. The strongest findings are with genes encoding alcohol metabolizing enzymes. A few candidate genes such as GABRA2 have shown robust associations with alcoholism. Moreover, it has become apparent that variants in stress-related genes such as CRHR1, may only confer risk in individuals exposed to trauma, particularly in early life. Over the past decade there have been tremendous advances in large scale SNP genotyping technologies allowing for genome-wide associations studies (GWAS). As a result, it is now recognized that genetic risk for alcoholism is likely to be due to common variants in very many genes, each of small effect, although rare variants with large effects might also play a role. This has resulted in a paradigm shift away from gene centric studies toward analyses of gene interactions and gene networks within biologically relevant pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Mary-Anne Enoch declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
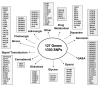
References
-
- Enoch M-A, Goldman D. The genetics of alcoholism and alcohol abuse. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2001;3:144–151. - PubMed
-
- [Accessed August 2013];National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC) Available at ( http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh29-2/74-78.htm) - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington DC: 1994.
-
- Koob GF. Alcoholism: allostasis and beyond. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:232–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

