The effect of moisture on the flowability of pharmaceutical excipients
- PMID: 24092523
- PMCID: PMC3909156
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-013-0036-0
The effect of moisture on the flowability of pharmaceutical excipients
Abstract
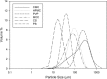
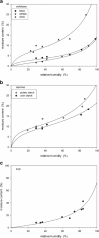
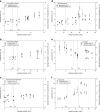
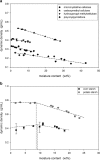
The effect of moisture content on flowability of six pharmaceutical powders (microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), corn starch, and potato starch) was investigated. Powder flowability was measured using established static techniques and emerging dynamic avalanche behavior measurements. Static techniques did not provide enough resolution to clearly identify changes in flowability due to increasing powder moisture content. Avalanche time and its standard deviation showed that flowability of MCC, CMC, PVP, and potato starch decreased after a critical moisture content, flowability of corn starch increased and flowability did not significantly change for HPMC. The moisture decreased flowability by forming stronger interparticle liquid bridges and increased flowability by acting as a lubricant. The dynamic density of the celluloses and PVP decreased linearly with increasing moisture content as the particles swelled with water. The starches also swelled and decreased in dynamic density, but only after a moisture content corresponding to monolayer coverage of water around the particles was reached. As flowability and dynamic density change with moisture content, to ensure consistent production of high-quality tablets, the moisture content of the powders must be measured and controlled.
Figures


References
-
- Callahan JC, Cleary GW, Elefant M, Kaplan G, Kensler T, Nash RA. Equilibrium moisture content of pharmaceutical powders. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1982;8:355–369. doi: 10.3109/03639048209022105. - DOI
-
- Malamataris S, Goidas P, Dimitriou A. Moisture sorption and tensile strength of some tableted direct compression excipients. Int J Pharm. 1991;68:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(91)90126-9. - DOI
-
- Brunauer S, Deming LS, Edwards Deming W, Teller E. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases. J Am Chem Soc. 1940;62:1723–1732. doi: 10.1021/ja01864a025. - DOI
-
- Donohue MD, Aranovich GL. Classification of Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Adv Colloid Interf Sci. 1998;76–77:137–152. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00044-X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

