Effects of a superoxide dismutase mimetic on biomarkers of lung angiogenesis and alveolarization during hyperoxia with intermittent hypoxia
- PMID: 24093057
- PMCID: PMC3786267
Effects of a superoxide dismutase mimetic on biomarkers of lung angiogenesis and alveolarization during hyperoxia with intermittent hypoxia
Abstract
Extremely premature neonates requiring oxygen therapy develop an accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), impaired alveolarization and dysmorphic pulmonary vasculature. Regulators of ROS (i.e. antioxidants), alveolarization (i.e. matrix metalloproteinases - MMPs) and microvascular maturation (i.e. vascular endothelial growth factor - VEGF) are altered in bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). We tested the hypothesis that early treatment with MnTBAP, a superoxide dismutase mimetic and superoxide anion and peroxynitrite scavenger, alters lung biomarkers of angiogenesis and alveolarization during hyperoxia with intermittent hypoxia (IH) in neonatal rats. Neonatal rats were exposed to 50% O2 with brief IH episodes (12% O2) from P0 to P14, or to room air (RA). On P0, P1 & P2, the pups received a daily IP injection of 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg MnTBAP, or saline. At P14, the pups were either euthanized, or allowed to recover in RA until P21. RA littermates were similarly treated. Lung VEGF, sVEGFR-1, MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 were determined. Low-dose MnTBAP (1 mg/kg) prevented the increase in lung VEGF induced by intermittent hypoxia noted in the control group. This dose was also effective for decreasing MMP-9 and MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio suggesting an anti-inflammatory effect for MnTBAP. IH decreased MMP-2 with no ameliorating effect by MnTBAP. Our data demonstrate that brief, repeated intermittent hypoxia during hyperoxia can alter biomarkers responsible for normal microvascular and alveolar development. In addition to prevention of hypoxic events, the use of antioxidants needs to be explored as a possible therapeutic intervention in neonates at risk for the development of oxidative lung injury.
Keywords: Antioxidants; hyperoxia; intermittent hypoxia; matrix metalloproteinases; tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase.
Figures
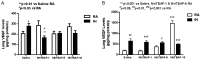
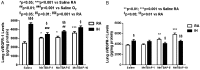
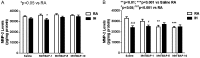


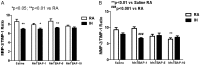

References
-
- Coalson JJ. Pathology of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol. 2003;8:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Ryan RM, Ahmed Q, Lakshminrusimha S. Inflammatory mediators in the immunobiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008;34:174–190. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt AJ, Pryhuber GS, Huyck H, Watkins RH, Metlay LA, Maniscalco WM. Disrupted pulmonary vasculature and decreased vascular endothelial growth factor, Flt-1, and TIE-2 in human infants dying with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1971–1980. - PubMed
-
- Coalson JJ, Winter V, DeLemos RA. Decreased alveolarization in baboon survivors with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:640–646. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
