Fundus-driven perimetry (microperimetry) compared to conventional static automated perimetry: similarities, differences, and clinical applications
- PMID: 24093180
- PMCID: PMC3792399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.03.021
Fundus-driven perimetry (microperimetry) compared to conventional static automated perimetry: similarities, differences, and clinical applications
Abstract
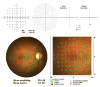
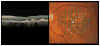
Fundus-driven perimetry, commonly known as microperimetry, is a technique for measuring visual field sensitivity, whilst simultaneously viewing the fundus. In this article, we review the technique, focusing on the MP-1 microperimeter (Nidek Instruments, Inc, Padua, Italy); we compare it with conventional static automated perimetry, emphasizing the importance of understanding the effects of the different stimulus conditions and data analyses on the interpretation of microperimetry data. The clinical applications of the technique, in the evaluation of functional and structural changes that accompany retinal diseases, are illustrated by its use in patients with age-related macular degeneration, Stargardt disease, and retinitis pigmentosa. In addition, the advantages and limitations of the technique are summarized.
© 2013 Canadian Ophthalmological Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson CA, Wall M, Thompson HS. A history of perimetry and visual field testing. Optom Vis Sci. 2011;88(1):8–15. - PubMed
-
- Inatomi A. A simple fundus perimetry with fundus camera. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser. 1979;19:359–62.
-
- Kani K, Eno N, Abe K, Ono T. Perimetry under television ophthalmoscopy. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser. 1977;14:231–6.
-
- Kani K, Ogita Y. Fundus controlled perimetry. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser. 1979;19:341–50.
-
- Timberlake GT, Mainster MA, Webb RH, Hughes GW, Trempe CL. Retinal localization of scotomata by scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982;22(1):91–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

