NADPH oxidases in lung health and disease
- PMID: 24093231
- PMCID: PMC4026303
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5608
NADPH oxidases in lung health and disease
Abstract
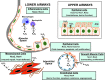
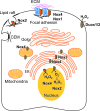
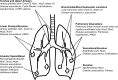
Significance: The evolution of the lungs and circulatory systems in vertebrates ensured the availability of molecular oxygen (O2; dioxygen) for aerobic cellular metabolism of internal organs in large animals. O2 serves as the physiologic terminal acceptor of mitochondrial electron transfer and of the NADPH oxidase (Nox) family of oxidoreductases to generate primarily water and reactive oxygen species (ROS), respectively.
Recent advances: The purposeful generation of ROS by Nox family enzymes suggests important roles in normal physiology and adaptation, most notably in host defense against invading pathogens and in cellular signaling.
Critical issues: However, there is emerging evidence that, in the context of chronic stress and/or aging, Nox enzymes contribute to the pathogenesis of a number of lung diseases.
Future directions: Here, we review evolving functions of Nox enzymes in normal lung physiology and emerging pathophysiologic roles in lung disease.
Figures

References
-
- Abdala-Valencia H, Earwood J, Bansal S, Jansen M, Babcock G, Garvy B, Wills-Karp M, and Cook-Mills JM. Nonhematopoietic NADPH oxidase regulation of lung eosinophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness in experimentally induced asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L1111–L1125, 2007 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akasaki T, Ohya Y, Kuroda J, Eto K, Abe I, Sumimoto H, and Iida M. Increased expression of gp91phox homologues of NAD(P)H oxidase in the aortic media during chronic hypertension: involvement of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertens Res 29: 813–820, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Amara N, Goven D, Prost F, Muloway R, Crestani B, and Boczkowski J. NOX4/NADPH oxidase expression is increased in pulmonary fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and mediates TGFbeta1-induced fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts. Thorax 65: 733–738, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

