Preliminary results in quantitation of HLA-DRA by real-time PCR: a promising approach to identify immunosuppression in sepsis
- PMID: 24093602
- PMCID: PMC4057202
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13046
Preliminary results in quantitation of HLA-DRA by real-time PCR: a promising approach to identify immunosuppression in sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: Reduced monocyte human leukocyte antigen (mHLA)-DR surface expression in the late phase of sepsis is postulated as a general biomarker of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and an independent predictor of nosocomial infections.
Methods: Fifty-nine patients with sepsis and blood culture growing pathogenic bacteria were studied. Blood samples were collected at day 1 or 2 after admission, for measurement of mHLA-DR by flow cytometry and mRNA expression of HLA-DRA and class II transactivator (CIITA) by qRT-PCR. Blood samples from blood donors were used as controls (n = 30).
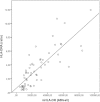
Results: A significant reduced expression of mHLA-DR, HLA-DRA, and CIITA was seen in septic patients compared with controls. HLA-DRA mRNA level in whole blood was highly correlated with surface expression of mHLA-DR.
Conclusions: Patients with sepsis display a diminished expression of HLA-DR at the monocyte surface as well as in the gene expression at the mRNA level. The mRNA expression level of HLA-DRA monitored by qRT-PCR correlates highly with surface expression of HLA-DR and appears to be a possible future biomarker for evaluation of immunosuppression in sepsis.
Figures


Comment in
-
Monocyte HLA-DR in sepsis: shall we stop following the flow?Crit Care. 2014 Jan 6;18(1):102. doi: 10.1186/cc13179. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24393356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb SA, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R. Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including the Pediatric S. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;17:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levy MM, Dellinger RP, Townsend SR, Linde-Zwirble WT, Marshall JC, Bion J, Schorr C, Artigas A, Ramsay G, Beale R, Parker MM, Gerlach H, Reinhart K, Silva E, Harvey M, Regan S, Angus DC. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign: results of an international guideline-based performance improvement program targeting severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2010;17:222–231. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1738-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

