Canonical Nlrp3 inflammasome links systemic low-grade inflammation to functional decline in aging
- PMID: 24093676
- PMCID: PMC4017327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.09.010
Canonical Nlrp3 inflammasome links systemic low-grade inflammation to functional decline in aging
Abstract
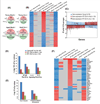
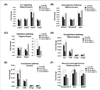
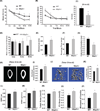
Despite a wealth of clinical data showing an association between inflammation and degenerative disorders in the elderly, the immune sensors that causally link systemic inflammation to aging remain unclear. Here we detail a mechanism by which the Nlrp3 inflammasome controls systemic low-grade age-related "sterile" inflammation in both periphery and brain independently of the noncanonical caspase-11 inflammasome. Ablation of Nlrp3 inflammasome protected mice from age-related increases in the innate immune activation, alterations in CNS transcriptome, and astrogliosis. Consistent with the hypothesis that systemic low-grade inflammation promotes age-related degenerative changes, the deficient Nlrp3 inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity improved glycemic control and attenuated bone loss and thymic demise. Notably, IL-1 mediated only Nlrp3 inflammasome-dependent improvement in cognitive function and motor performance in aged mice. These studies reveal Nlrp3 inflammasome as an upstream target that controls age-related inflammation and offer an innovative therapeutic strategy to lower Nlrp3 activity to delay multiple age-related chronic diseases.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Axtell RC, Steinman L. Gaining entry to an uninflamed brain. Nat. Immunol. 2009;10:453–455. - PubMed
-
- Brazma A, Hingamp P, Quackenbush J, Sherlock G, Spellman P, Stoeckert C, Aach J, Ansorge W, Ball CA, Caust HC, et al. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)-toward standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 2001;29:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power SE, O'Connor EM, Cusack S, Harris HM, Coakley M, Lakshminarayanan B, O'Sullivan O, et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature. 2012;488:178–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HD055528/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD055528/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR02195/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK090556/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090556/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI105097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AG043608/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 8P20 GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043608/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI105097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

