Computational approaches to species phylogeny inference and gene tree reconciliation
- PMID: 24094331
- PMCID: PMC3855310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tree.2013.09.004
Computational approaches to species phylogeny inference and gene tree reconciliation
Abstract
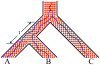
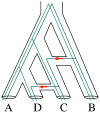
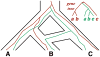
An intricate relation exists between gene trees and species phylogenies, due to evolutionary processes that act on the genes within and across the branches of the species phylogeny. From an analytical perspective, gene trees serve as character states for inferring accurate species phylogenies, and species phylogenies serve as a backdrop against which gene trees are contrasted for elucidating evolutionary processes and parameters. In a 1997 paper, Maddison discussed this relation, reviewed the signatures left by three major evolutionary processes on the gene trees, and surveyed parsimony and likelihood criteria for utilizing these signatures to elucidate computationally this relation. Here, I review progress that has been made in developing computational methods for analyses under these two criteria, and survey remaining challenges.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
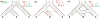
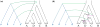
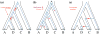
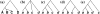
References
-
- Dittmar K, Liberles D, editors. Evolution after Gene Duplication. Wiley-Blackwell; Hoboken, New Jersey: 2010.
-
- Innan H, Kondrashov F. The evolution of gene duplications: classifying and distinguishing between models. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2010;11:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Abbott R, Rieseberg L. eLS. 2012. Hybrid speciation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

