TRF2 interaction with Ku heterotetramerization interface gives insight into c-NHEJ prevention at human telomeres
- PMID: 24095731
- PMCID: PMC3984498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.08.040
TRF2 interaction with Ku heterotetramerization interface gives insight into c-NHEJ prevention at human telomeres
Abstract
Telomeres are protected from nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) to avoid deleterious chromosome fusions, yet they associate with the Ku heterodimer that is principal in the classical NHEJ (c-NHEJ) pathway. T-loops have been proposed to inhibit Ku's association with telomeric ends, thus inhibiting c-NHEJ; however, deficiencies in the t-loop model suggest additional mechanisms are in effect. We demonstrate that TRF2 interacts with Ku at telomeres and via residues in Ku70 helix 5 (α5), which are vital for NHEJ. We show that Ku's interaction with a TRF2 mutant that induces telomeric fusions is significantly impaired. Additionally, we demonstrate that Ku70 α5 is required for Ku self-association in live cells, which can bridge DNA ends. Together, these findings lead us to propose a model in which telomeres are directly protected from c-NHEJ via TRF2 impeding Ku's ability to synapse telomere ends.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
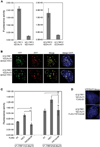

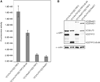
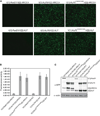



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM084897/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077509/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM077509/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG034764/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31AG034764/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12GM084897/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

