Vitamin D and DBP: the free hormone hypothesis revisited
- PMID: 24095930
- PMCID: PMC3976473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.09.012
Vitamin D and DBP: the free hormone hypothesis revisited
Abstract
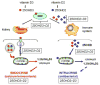
The last five years have witnessed a remarkable renaissance in vitamin D research and a complete re-evaluation of its benefits to human health. Two key factors have catalyzed these changes. First, it now seems likely that localized, tissue-specific, conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) drives many of the newly recognized effects of vitamin D on human health. The second key factor concerns the ongoing discussion as to what constitutes adequate or optimal serum vitamin D (25OHD) status, with the possibility that vitamin D-deficiency is common to communities across the globe. These two concepts appear to be directly linked when low serum concentrations of 25OHD compromise intracrine generation of 1,25(OH)2D within target tissues. But, is this an over-simplification? Pro-hormone 25OHD is a lipophilic molecule that is transported in the circulation bound primarily to vitamin D binding protein (DBP). While the association between 25OHD and DBP is pivotal for renal handling of 25OHD and endocrine synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D, what is the role of DBP for extra-renal synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D? We hypothesize that binding to DBP impairs delivery of 25OHD to the vitamin D-activating enzyme 1α-hydroxylase in some target cells. Specifically, it is unbound, 'free' 25OHD that drives many of the non-classical actions of vitamin D. Levels of 'free' 25OHD are dependent on the concentration of DBP and alternative serum binding proteins such as albumin, but will also be influenced by variations in DBP binding affinity for specific vitamin D metabolites. The aim of this review will be to discuss the merits of 'free 25OHD' as an alternative marker of vitamin D status, particularly in the context of non-classical responses to vitamin D. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled '16th Vitamin D Workshop'.
Keywords: Bioavailable; Free hormone; Intracrine; Megalin; Vitamin D; Vitamin D binding protein.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no disclosures to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Orchinik M, Hastings N, Witt D, McEwen BS. High-affinity binding of corticosterone to mammalian neuronal membranes: possible role of corticosteroid binding globulin. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology. 1997;60(3–4):229–236. - PubMed
-
- Khan MS, Hryb DJ, Hashim GA, Romas NA, Rosner W. Delineation and synthesis of the membrane receptor-binding domain of sex hormone-binding globulin. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1990;265(30):18362–18365. - PubMed
-
- Hammond GL. Potential functions of plasma steroid-binding proteins. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM. 1995;6(9–10):298–304. - PubMed
-
- Rosner W, Hryb DJ, Khan MS, Nakhla AM, Romas NA. Androgen and estrogen signaling at the cell membrane via G-proteins and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Steroids. 1999;64(1–2):100–106. - PubMed
-
- Rosner W, Hryb DJ, Khan MS, Nakhla AM, Romas NA. Sex hormone-binding globulin mediates steroid hormone signal transduction at the plasma membrane. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology. 1999;69(1–6):481–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

