Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress: 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance
- PMID: 24096871
- PMCID: PMC3824598
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2013.138
Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress: 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance
Abstract
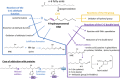
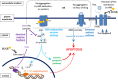
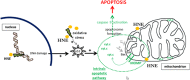
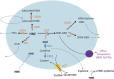
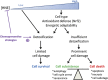
During the last three decades, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE), a major α,β-unsaturated aldehyde product of n-6 fatty acid oxidation, has been shown to be involved in a great number of pathologies such as metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and cancers. These multiple pathologies can be explained by the fact that HNE is a potent modulator of numerous cell processes such as oxidative stress signaling, cell proliferation, transformation or cell death. The main objective of this review is to focus on the different aspects of HNE-induced cell death, with a particular emphasis on apoptosis. HNE is a special apoptotic inducer because of its abilities to form protein adducts and to propagate oxidative stress. It can stimulate intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways and interact with typical actors such as tumor protein 53, JNK, Fas or mitochondrial regulators. At the same time, due to its oxidant status, it can also induce some cellular defense mechanisms against oxidative stress, thus being involved in its own detoxification. These processes in turn limit the apoptotic potential of HNE. These dualities can imbalance cell fate, either toward cell death or toward survival, depending on the cell type, the metabolic state and the ability to detoxify.
Figures
References
-
- Schaur RJ. Basic aspects of the biochemical reactivity of 4-hydroxynonenal. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Duryee MJ, Willis MS, Freeman TL, Kuszynski CA, Tuma DJ, Klassen LW, et al. Mechanisms of alcohol liver damage: aldehydes, scavenger receptors, and autoimmunity. Front Bio sci. 2004;9:3145–3155. - PubMed
-
- Poli G, Schaur RJ, Siems WG, Leonarduzzi G. 4-hydroxynonenal: a membrane lipid oxidation product of medicinal interest. Med Res Rev. 2008;28:569–631. - PubMed
-
- Uchida K, Toyokuni S, Nishikawa K, Kawakishi S, Oda H, Hiai H, et al. Michael addition-type 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal adducts in modified low-density lipoproteins: markers for atherosclerosis. Biochemistry. 1994;33:12487–12494. - PubMed
-
- Pierre F, Peiro G, Tache S, Cross AJ, Bingham SA, Gasc N, et al. New marker of colon cancer risk associated with heme intake: 1,4-dihydroxynonane mercapturic acid. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:2274–2279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

