Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels
Affiliations
- 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 2 Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 3 Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 4 Center for Statistical Genetics, Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 5 Department of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 6 Center for Human Genetic Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 7 Broad Institute, Program in Medical and Population Genetics, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, USA.
- 8 Department of Medical Sciences, Molecular Epidemiology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 9 Science for Life Laboratory, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 10 Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, CB10 1SA, Hinxton, United Kingdom.
- 11 Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 12 Department of Genetics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 USA.
- 13 Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, 900 Commonwealth Ave., Boston MA 02215, USA.
- 14 Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115, USA.
- 15 Service of Medical Genetics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 16 Department of Medical Genetics, University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 17 Division of Preventive Medicine and Health Services Research, Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Zhunan, Taiwan.
- 18 Genetic Epidemiology Unit, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 19 Department of Neurology, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 20 Medical Research Institute, University of Dundee, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School. Dundee, DD1 9SY, United Kingdom.
- 21 Cardiology, Department of Specialities of Medicine, Geneva University Hospital, Rue Gabrielle-Perret-Gentil 4, 1211 Geneva 14, Switzerland.
- 22 Center for Complex Disease Genomics, McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
- 23 Estonian Genome Center of the University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia.
- 24 Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia.
- 25 Department of Genetics, Washington University School of Medicine, USA.
- 26 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7BN, United Kingdom.
- 27 Centre for Population Health Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Teviot Place, Edinburgh, EH8 9AG, Scotland, United Kingdom.
- 28 Department of Public Health and Primary Care, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
- 29 Hjelt Institute, Department of Public Health, University of Helsinki, Finland.
- 30 Centre For Paediatric Epidemiology and Biostatistics/MRC Centre of Epidemiology for Child Health, University College of London Institute of Child Health, London, United Kingdom.
- 31 Centre for Medical Systems Biology, Leiden, the Netherlands.
- 32 Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 33 Uppsala Clinical Research Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 34 Genome Centre, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK.
- 35 Clinical Pharmacology, NIHR Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit, William Harvey Research Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry Queen Mary University of London, London, UK.
- 36 Biocenter Oulu, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.
- 37 Institute of Health Sciences, University of Oulu, Finland.
- 38 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland FIMM, University of Helsinki, Finland.
- 39 Public Health Genomics Unit, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 40 Department of Internal Medicine II - Cardiology, University of Ulm Medical Centre, Ulm, Germany.
- 41 Mannheim Institute of Public Health, Social and Preventive Medicine, Medical Faculty of Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Ludolf-Krehl-Strasse 7-11, 68167 Mannheim, Germany.
- 42 Medical Genetics Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA.
- 43 MRC Epidemiology Unit, Institute of Metabolic Science, Box 285, Addenbrooke's Hospital, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 0QQ, United Kingdom.
- 44 Department of Clinical Chemistry, Fimlab Laboratories, Tampere 33520, Finland.
- 45 Department of Clinical Chemistry, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tampere 33014, Finland.
- 46 Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology, King's College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 47 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland, School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
- 48 Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 49 Department of Medicine I, University Hospital Grosshadern, Ludwig-Maximilians University, Munich, Germany.
- 50 Institute of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich, Munich, Germany.
- 51 Department of Epidemiology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 52 Division of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 53 Division of Genetics, Program in Genomics, Children's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 54 Istituto di Ricerca Genetica e Biomedica, CNR, Monserrato, 09042, Italy.
- 55 Massachusetts General Hospital/Broad Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA.
- 56 Center for Neurobehavioral Genetics, The Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior, University of California, Los Angeles, USA.
- 57 Genetic Epidemiology Group, Deparment of Epidemiology and Public Health, UCL, London WC1E 6BT, United Kingdom.
- 58 Department of Clinical Sciences, Genetic & Molecular Epidemiology Unit, Lund University Diabetes Center, Scania University Hosptial, Malmö, Sweden.
- 59 Department of Odontology, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 60 Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Unit of Medicine, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 61 Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Universita di Sassari, 07100 SS, Italy.
- 62 Atherosclerosis Research Unit, Department of Medicine Solna, Karolinska University Hospital, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 63 Center for Molecular Medicine, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 64 Clinical Research Branch, National Institute Health, Baltimore, MD, USA.
- 65 deCODE Genetics/Amgen, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 66 Department of Genetics, University of Pennsylvania - School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA, 19104, USA.
- 67 Department of Systems Pharmacology and Translational Therapeutics, University of Pennsylvania - School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA, 19104, USA.
- 68 Human Genetics Center, University of Texas Health Science Center - School of Public Health, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
- 69 HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, Huntsville, AL, USA.
- 70 MRC Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing, 33 Bedford Place, London, WC1B 5JU, United Kingdom.
- 71 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 72 Ealing Hospital, Southall, Middlesex UB1 3HW, United Kingdom.
- 73 MRC/UVRI Uganda Research Unit on AIDS, Entebbe, Uganda.
- 74 University of Cambridge Metabolic Research Laboratories and NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, Level 4, Institute of Metabolic Science Box 289 Addenbrooke's Hospital Cambridge CB2 OQQ, UK.
- 75 Department of Pediatrics, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, USA.
- 76 Genome Technology Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, NIH, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
- 77 Department of Experimental Medicine, University of Milano Bicocca, Italy.
- 78 MedStar Health Research Institute, 6525 Belcrest Road, Suite 700, Hyattsville, MD 20782, USA.
- 79 Research Centre on Public Health, University of Milano Bicocca, Italy.
- 80 Department of Dietetics-Nutrition, Harokopio University, 70 El. Venizelou Str, Athens, Greece.
- 81 Institute of Epidemiology I, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 82 Institute of Epidemiology II, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 83 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, MRC Health Protection Agency (HPA) Centre for Environment and Health, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, UK.
- 84 The Laboratory in Mjodd, 108 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 85 Division of Cardiovascular Epidemiology, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 86 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA.
- 87 Research Unit of Molecular Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 88 Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Oxford, OX3 7LJ, United Kingdom.
- 89 Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Nutritional research, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 90 Department of Clinical Sciences/Obstetrics and Gynecology, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 91 MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom.
- 92 Laboratory of Neurogenetics, National Institute on Aging, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
- 93 Center for Biomedicine, European Academy Bozen/Bolzano (EURAC), Bolzano, Italy - Affiliated Institute of the University of Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany.
- 94 Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 95 Hannover Unified Biobank, Hannover Medical School, Hannover 30625, Germany.
- 96 Department of Vascular Medicine, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 97 Clinical Gerontology Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
- 98 Kuopio Research Institute of Exercise Medicine, Kuopio, Finland.
- 99 Division of Endocrine and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 100 Diabetes Prevention Unit, National Institute for Health and Welfare, 00271 Helsinki, Finland.
- 101 The Genetics of Obesity and Related Metabolic Traits Program, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA.
- 102 The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at ount Sinai, New York, USA.
- 103 The Mindich Child Health and Development Institute, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
- 104 School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, Oakfield House, Oakfield Grove, Bristol BS8 2BN, United Kingdom.
- 105 Institute for Medical Informatics and Biometrics, University of Dresden, Medical Faculty Carl Gustav Carus, Fetscherstrasse 74, 01307 Dresden, Germany.
- 106 Laboratory of Genetics, National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, MD21224, USA.
- 107 Department of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tamperew 33014, Finland.
- 108 Department of Internal Medicine, Päijät-Häme Central Hospital, Lahti, Finland.
- 109 Division of Cardiology, Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland.
- 110 Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Landspitali University Hospital, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 111 Department of Medical Genetics, Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland.
- 112 Genetic Epidemiology Group, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge, United ingdom.
- 113 Department of Statistical Sciences, University College of London, London, United Kingdom.
- 114 National Institute for Health and Welfare, Oulu, Finland.
- 115 Cardiovascular Institute, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, 3400 Civic Center Blvd, Building 421, Translational Research Center, Philadelphia, PA 19104-5158, USA.
- 116 Division of Translational Medicine and Human Genetics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, 3400 Civic Center Blvd, Building 421, Translational Research Center, Philadelphia, PA 19104-5158, USA.
- 117 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- 118 Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- 119 Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)-sponsored Netherlands Consortium for Healthy Aging NCHA), Leiden, The Netherlands.
- 120 Department of Clinical Sciences/Clinical Chemistry, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.
- 121 National Institute for Health Research Leicester Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK.
- 122 Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester, LE3 9QP, UK.
- 123 Clinical Institute of Medical and Chemical Laboratory Diagnostics, Medical University of Graz, Austria.
- 124 School of International Development, University of East Anglia, Norwich NR4 7TJ, United Kingdom.
- 125 University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 126 INSERM UMRS 937, Pierre and Marie Curie University, Paris, France.
- 127 Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 128 LifeLines Cohort Study, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 129 Department of Genetics, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 130 Department of Biological Psychology, VU Univ, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 131 Department of Community Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway.
- 132 Department of Nutrition, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.
- 133 Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, EA 3430, University of Strasbourg, Faculty of Medicine, Strasbourg, France.
- 134 Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
- 135 Geriatric Unit, Azienda Sanitaria Firenze (ASF), Florence, Italy.
- 136 Chemical Pathology, Department of Pathology, University of the West Indies, Mona, Kingston 7, Jamaica.
- 137 Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine (IUMSP), Lausanne University Hospital, Route de la Corniche 10, 1010 Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 138 Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Department of Internal Medicine, Ulm University Medical Centre, Ulm, Germany.
- 139 Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
- 140 Department of Medicine III, University of Dresden, Medical Faculty Carl Gustav Carus, Fetscherstrasse 74, 01307 Dresden, Germany.
- 141 Ministry of Health, Victoria, Republic of Seychelles.
- 142 Service of Nephrology, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 143 Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, United Kingdom.
- 144 Division of Reproductive Endocrinology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, USA.
- 145 Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, USA.
- 146 Department of Preventive Medicine and Epidemiology, Loyola University Medical School, Maywood, Illinois 60153, USA.
- 147 Office of Population Studies Foundation, University of San Carlos, Talamban, Cebu City, Philippines.
- 148 Department of Cardiology, Toulouse University School of Medicine, Rangueil Hospital, Toulouse, France.
- 149 Department of Psychiatry, University of California, Los Angeles, USA.
- 150 Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, SE-20502, Malmö, Sweden.
- 151 Department of Medicine, Helsinki University Hospital, FI-00029 Helsinki, Finland.
- 152 Icelandic Heart Association, Kopavogur, Iceland.
- 153 Department of Cardiology, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 154 Laboratory of Epidemiology, Demography, and Biometry, National Institute on Ageing, Bethesda, MD, USA.
- 155 Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Zhunan, Taiwan.
- 156 Cardiovascular Genetics, BHF Laboratories, Institute Cardiovascular Science, University College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 157 Cardiovascular Genetics, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT, USA.
- 158 HUNT Research Centre, Department of Public Health and General Practice, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Levanger, Norway.
- 159 Kaiser Permanente, Division of Research, Oakland, CA, USA.
- 160 Unit of Primary Care, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 161 Department of Chronic Disease Prevention, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Turku, Finland.
- 162 Department of Clinical Physiology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tampere 33014, Finland.
- 163 Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 164 Institute of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Oulu and Clinical Research Center, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 165 National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College London, Hammersmith Hospital, London, United Kingdom.
- 166 Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute, 5700 Martin Luther King Junior Way, Oakland, CA 94609, USA.
- 167 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 168 Institute of Regional Health Services Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.
- 169 Odense Patient data Explorative Network (OPEN), Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark.
- 170 Institute of Biomedicine/Physiology, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio Campus, Finland.
- 171 Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 172 Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Locked Bag 2000, Royal Brisbane Hospital, Queensland 4029, Australia.
- 173 Synlab Academy, Synlab Services GmbH,Gottlieb-Daimler-Straße 25, 68165 Mannheim, Germany.
- 174 Tropical Metabolism Research Unit, Tropical Medicine Research Institute, University of the West Indies, Mona, Kingston 7, Jamaica.
- 175 U872 Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, 75006 Paris, France.
- 176 Department of Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 177 Department of Neurology, General Central Hospital, Bolzano, Italy.
- 178 Department of Neurology, University of Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany.
- 179 Cardiovascular Health Research Unit, Departments of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Services, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
- 180 Group Health Research Institute, Group Health Cooperative, Seattle, WA, USA.
- 181 Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 182 Center for Non-Communicable Diseases, Karachi, Pakistan.
- 183 Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, USA.
- 184 Unit of Chronic Disease Epidemiology and Prevention, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 185 South Karelia Central Hospital, Lappeenranta, Finland.
- 186 Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden, German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), Dresden, Germany.
- 187 Division of Endocrine and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
- 188 Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center, Veterans Administration Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland.
- 189 Faculty of Medicine, University of Iceland, 101 Reykjavík, Iceland.
- 190 Division of Population Health Sciences and Education, St George's, University of London, Cranmer Terrace, London SW17 0RE, United Kingdom.
- 191 Department of Pharmacological Sciences, University of Milan, Monzino Cardiology Center, IRCCS, Milan, Italy.
- 192 Centre for Vascular Prevention, Danube-University Krems, 3500 Krems, Austria.
- 193 King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Medicine, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia.
- 194 Red RECAVA Grupo RD06/0014/0015, Hospital Universitario La Paz, 28046.
- 195 Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, University of Eastern Finland, Finland.
- 196 Research Unit, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 197 Department of Medicine, Lausanne University Hospital, Switzerland.
- 198 Department of Endocrinology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 199 Department of Cardiovascular Epidemiology and Population Genetics, National Center for rdiovascular Investigation, Madrid, Spain.
- 200 IMDEA-Alimentacion, Madrid, Spain.
- 201 Nutrition and Genomics Laboratory, Jean Mayer-USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA.
- 202 Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA.
- 203 Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, MA, USA.
- 204 Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA.
- 205 Cardiovascular Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 206 Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- PMID: 24097068
- PMCID: PMC3838666
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2797
Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels
Authors
Affiliations
- 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 2 Department of Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 3 Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 4 Center for Statistical Genetics, Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109, USA.
- 5 Department of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts 02118, USA.
- 6 Center for Human Genetic Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 7 Broad Institute, Program in Medical and Population Genetics, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, USA.
- 8 Department of Medical Sciences, Molecular Epidemiology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 9 Science for Life Laboratory, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 10 Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, CB10 1SA, Hinxton, United Kingdom.
- 11 Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 12 Department of Genetics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 USA.
- 13 Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, 900 Commonwealth Ave., Boston MA 02215, USA.
- 14 Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115, USA.
- 15 Service of Medical Genetics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 16 Department of Medical Genetics, University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 17 Division of Preventive Medicine and Health Services Research, Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Zhunan, Taiwan.
- 18 Genetic Epidemiology Unit, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 19 Department of Neurology, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
- 20 Medical Research Institute, University of Dundee, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School. Dundee, DD1 9SY, United Kingdom.
- 21 Cardiology, Department of Specialities of Medicine, Geneva University Hospital, Rue Gabrielle-Perret-Gentil 4, 1211 Geneva 14, Switzerland.
- 22 Center for Complex Disease Genomics, McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
- 23 Estonian Genome Center of the University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia.
- 24 Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia.
- 25 Department of Genetics, Washington University School of Medicine, USA.
- 26 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7BN, United Kingdom.
- 27 Centre for Population Health Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Teviot Place, Edinburgh, EH8 9AG, Scotland, United Kingdom.
- 28 Department of Public Health and Primary Care, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
- 29 Hjelt Institute, Department of Public Health, University of Helsinki, Finland.
- 30 Centre For Paediatric Epidemiology and Biostatistics/MRC Centre of Epidemiology for Child Health, University College of London Institute of Child Health, London, United Kingdom.
- 31 Centre for Medical Systems Biology, Leiden, the Netherlands.
- 32 Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 33 Uppsala Clinical Research Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 34 Genome Centre, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK.
- 35 Clinical Pharmacology, NIHR Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit, William Harvey Research Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry Queen Mary University of London, London, UK.
- 36 Biocenter Oulu, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.
- 37 Institute of Health Sciences, University of Oulu, Finland.
- 38 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland FIMM, University of Helsinki, Finland.
- 39 Public Health Genomics Unit, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 40 Department of Internal Medicine II - Cardiology, University of Ulm Medical Centre, Ulm, Germany.
- 41 Mannheim Institute of Public Health, Social and Preventive Medicine, Medical Faculty of Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Ludolf-Krehl-Strasse 7-11, 68167 Mannheim, Germany.
- 42 Medical Genetics Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA.
- 43 MRC Epidemiology Unit, Institute of Metabolic Science, Box 285, Addenbrooke's Hospital, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 0QQ, United Kingdom.
- 44 Department of Clinical Chemistry, Fimlab Laboratories, Tampere 33520, Finland.
- 45 Department of Clinical Chemistry, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tampere 33014, Finland.
- 46 Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology, King's College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 47 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland, School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
- 48 Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 49 Department of Medicine I, University Hospital Grosshadern, Ludwig-Maximilians University, Munich, Germany.
- 50 Institute of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich, Munich, Germany.
- 51 Department of Epidemiology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 52 Division of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 53 Division of Genetics, Program in Genomics, Children's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- 54 Istituto di Ricerca Genetica e Biomedica, CNR, Monserrato, 09042, Italy.
- 55 Massachusetts General Hospital/Broad Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA.
- 56 Center for Neurobehavioral Genetics, The Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior, University of California, Los Angeles, USA.
- 57 Genetic Epidemiology Group, Deparment of Epidemiology and Public Health, UCL, London WC1E 6BT, United Kingdom.
- 58 Department of Clinical Sciences, Genetic & Molecular Epidemiology Unit, Lund University Diabetes Center, Scania University Hosptial, Malmö, Sweden.
- 59 Department of Odontology, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 60 Department of Public Health and Primary Care, Unit of Medicine, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 61 Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Universita di Sassari, 07100 SS, Italy.
- 62 Atherosclerosis Research Unit, Department of Medicine Solna, Karolinska University Hospital, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 63 Center for Molecular Medicine, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 64 Clinical Research Branch, National Institute Health, Baltimore, MD, USA.
- 65 deCODE Genetics/Amgen, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 66 Department of Genetics, University of Pennsylvania - School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA, 19104, USA.
- 67 Department of Systems Pharmacology and Translational Therapeutics, University of Pennsylvania - School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA, 19104, USA.
- 68 Human Genetics Center, University of Texas Health Science Center - School of Public Health, Houston, TX 77030, USA.
- 69 HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, Huntsville, AL, USA.
- 70 MRC Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing, 33 Bedford Place, London, WC1B 5JU, United Kingdom.
- 71 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 72 Ealing Hospital, Southall, Middlesex UB1 3HW, United Kingdom.
- 73 MRC/UVRI Uganda Research Unit on AIDS, Entebbe, Uganda.
- 74 University of Cambridge Metabolic Research Laboratories and NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, Level 4, Institute of Metabolic Science Box 289 Addenbrooke's Hospital Cambridge CB2 OQQ, UK.
- 75 Department of Pediatrics, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, USA.
- 76 Genome Technology Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, NIH, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
- 77 Department of Experimental Medicine, University of Milano Bicocca, Italy.
- 78 MedStar Health Research Institute, 6525 Belcrest Road, Suite 700, Hyattsville, MD 20782, USA.
- 79 Research Centre on Public Health, University of Milano Bicocca, Italy.
- 80 Department of Dietetics-Nutrition, Harokopio University, 70 El. Venizelou Str, Athens, Greece.
- 81 Institute of Epidemiology I, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 82 Institute of Epidemiology II, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 83 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, MRC Health Protection Agency (HPA) Centre for Environment and Health, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, UK.
- 84 The Laboratory in Mjodd, 108 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 85 Division of Cardiovascular Epidemiology, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 86 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA.
- 87 Research Unit of Molecular Epidemiology, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Neuherberg 85764, Germany.
- 88 Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Oxford, OX3 7LJ, United Kingdom.
- 89 Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Nutritional research, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden.
- 90 Department of Clinical Sciences/Obstetrics and Gynecology, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 91 MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom.
- 92 Laboratory of Neurogenetics, National Institute on Aging, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
- 93 Center for Biomedicine, European Academy Bozen/Bolzano (EURAC), Bolzano, Italy - Affiliated Institute of the University of Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany.
- 94 Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 95 Hannover Unified Biobank, Hannover Medical School, Hannover 30625, Germany.
- 96 Department of Vascular Medicine, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 97 Clinical Gerontology Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
- 98 Kuopio Research Institute of Exercise Medicine, Kuopio, Finland.
- 99 Division of Endocrine and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 100 Diabetes Prevention Unit, National Institute for Health and Welfare, 00271 Helsinki, Finland.
- 101 The Genetics of Obesity and Related Metabolic Traits Program, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA.
- 102 The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine, The Icahn School of Medicine at ount Sinai, New York, USA.
- 103 The Mindich Child Health and Development Institute, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
- 104 School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, Oakfield House, Oakfield Grove, Bristol BS8 2BN, United Kingdom.
- 105 Institute for Medical Informatics and Biometrics, University of Dresden, Medical Faculty Carl Gustav Carus, Fetscherstrasse 74, 01307 Dresden, Germany.
- 106 Laboratory of Genetics, National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, MD21224, USA.
- 107 Department of Clinical Pharmacology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tamperew 33014, Finland.
- 108 Department of Internal Medicine, Päijät-Häme Central Hospital, Lahti, Finland.
- 109 Division of Cardiology, Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland.
- 110 Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Landspitali University Hospital, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland.
- 111 Department of Medical Genetics, Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland.
- 112 Genetic Epidemiology Group, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge, United ingdom.
- 113 Department of Statistical Sciences, University College of London, London, United Kingdom.
- 114 National Institute for Health and Welfare, Oulu, Finland.
- 115 Cardiovascular Institute, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, 3400 Civic Center Blvd, Building 421, Translational Research Center, Philadelphia, PA 19104-5158, USA.
- 116 Division of Translational Medicine and Human Genetics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, 3400 Civic Center Blvd, Building 421, Translational Research Center, Philadelphia, PA 19104-5158, USA.
- 117 Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- 118 Department of Internal Medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- 119 Netherlands Genomics Initiative (NGI)-sponsored Netherlands Consortium for Healthy Aging NCHA), Leiden, The Netherlands.
- 120 Department of Clinical Sciences/Clinical Chemistry, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.
- 121 National Institute for Health Research Leicester Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK.
- 122 Department of Cardiovascular Sciences, University of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester, LE3 9QP, UK.
- 123 Clinical Institute of Medical and Chemical Laboratory Diagnostics, Medical University of Graz, Austria.
- 124 School of International Development, University of East Anglia, Norwich NR4 7TJ, United Kingdom.
- 125 University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 126 INSERM UMRS 937, Pierre and Marie Curie University, Paris, France.
- 127 Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 128 LifeLines Cohort Study, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 129 Department of Genetics, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 130 Department of Biological Psychology, VU Univ, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- 131 Department of Community Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway.
- 132 Department of Nutrition, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.
- 133 Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, EA 3430, University of Strasbourg, Faculty of Medicine, Strasbourg, France.
- 134 Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
- 135 Geriatric Unit, Azienda Sanitaria Firenze (ASF), Florence, Italy.
- 136 Chemical Pathology, Department of Pathology, University of the West Indies, Mona, Kingston 7, Jamaica.
- 137 Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine (IUMSP), Lausanne University Hospital, Route de la Corniche 10, 1010 Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 138 Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Department of Internal Medicine, Ulm University Medical Centre, Ulm, Germany.
- 139 Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
- 140 Department of Medicine III, University of Dresden, Medical Faculty Carl Gustav Carus, Fetscherstrasse 74, 01307 Dresden, Germany.
- 141 Ministry of Health, Victoria, Republic of Seychelles.
- 142 Service of Nephrology, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland.
- 143 Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, United Kingdom.
- 144 Division of Reproductive Endocrinology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, USA.
- 145 Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, USA.
- 146 Department of Preventive Medicine and Epidemiology, Loyola University Medical School, Maywood, Illinois 60153, USA.
- 147 Office of Population Studies Foundation, University of San Carlos, Talamban, Cebu City, Philippines.
- 148 Department of Cardiology, Toulouse University School of Medicine, Rangueil Hospital, Toulouse, France.
- 149 Department of Psychiatry, University of California, Los Angeles, USA.
- 150 Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, SE-20502, Malmö, Sweden.
- 151 Department of Medicine, Helsinki University Hospital, FI-00029 Helsinki, Finland.
- 152 Icelandic Heart Association, Kopavogur, Iceland.
- 153 Department of Cardiology, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 154 Laboratory of Epidemiology, Demography, and Biometry, National Institute on Ageing, Bethesda, MD, USA.
- 155 Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Zhunan, Taiwan.
- 156 Cardiovascular Genetics, BHF Laboratories, Institute Cardiovascular Science, University College London, London, United Kingdom.
- 157 Cardiovascular Genetics, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT, USA.
- 158 HUNT Research Centre, Department of Public Health and General Practice, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Levanger, Norway.
- 159 Kaiser Permanente, Division of Research, Oakland, CA, USA.
- 160 Unit of Primary Care, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 161 Department of Chronic Disease Prevention, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Turku, Finland.
- 162 Department of Clinical Physiology, University of Tampere School of Medicine, Tampere 33014, Finland.
- 163 Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 164 Institute of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Oulu and Clinical Research Center, Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland.
- 165 National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College London, Hammersmith Hospital, London, United Kingdom.
- 166 Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute, 5700 Martin Luther King Junior Way, Oakland, CA 94609, USA.
- 167 Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital, 70210 Kuopio, Finland.
- 168 Institute of Regional Health Services Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.
- 169 Odense Patient data Explorative Network (OPEN), Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark.
- 170 Institute of Biomedicine/Physiology, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio Campus, Finland.
- 171 Department of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
- 172 Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Locked Bag 2000, Royal Brisbane Hospital, Queensland 4029, Australia.
- 173 Synlab Academy, Synlab Services GmbH,Gottlieb-Daimler-Straße 25, 68165 Mannheim, Germany.
- 174 Tropical Metabolism Research Unit, Tropical Medicine Research Institute, University of the West Indies, Mona, Kingston 7, Jamaica.
- 175 U872 Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, 75006 Paris, France.
- 176 Department of Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 177 Department of Neurology, General Central Hospital, Bolzano, Italy.
- 178 Department of Neurology, University of Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany.
- 179 Cardiovascular Health Research Unit, Departments of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Services, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
- 180 Group Health Research Institute, Group Health Cooperative, Seattle, WA, USA.
- 181 Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 182 Center for Non-Communicable Diseases, Karachi, Pakistan.
- 183 Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, USA.
- 184 Unit of Chronic Disease Epidemiology and Prevention, National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
- 185 South Karelia Central Hospital, Lappeenranta, Finland.
- 186 Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden, German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), Dresden, Germany.
- 187 Division of Endocrine and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
- 188 Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center, Veterans Administration Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland.
- 189 Faculty of Medicine, University of Iceland, 101 Reykjavík, Iceland.
- 190 Division of Population Health Sciences and Education, St George's, University of London, Cranmer Terrace, London SW17 0RE, United Kingdom.
- 191 Department of Pharmacological Sciences, University of Milan, Monzino Cardiology Center, IRCCS, Milan, Italy.
- 192 Centre for Vascular Prevention, Danube-University Krems, 3500 Krems, Austria.
- 193 King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Medicine, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia.
- 194 Red RECAVA Grupo RD06/0014/0015, Hospital Universitario La Paz, 28046.
- 195 Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, University of Eastern Finland, Finland.
- 196 Research Unit, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 197 Department of Medicine, Lausanne University Hospital, Switzerland.
- 198 Department of Endocrinology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, The Netherlands.
- 199 Department of Cardiovascular Epidemiology and Population Genetics, National Center for rdiovascular Investigation, Madrid, Spain.
- 200 IMDEA-Alimentacion, Madrid, Spain.
- 201 Nutrition and Genomics Laboratory, Jean Mayer-USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA.
- 202 Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA.
- 203 Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, MA, USA.
- 204 Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA.
- 205 Cardiovascular Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.
- 206 Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
- PMID: 24097068
- PMCID: PMC3838666
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2797
Abstract
Levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides and total cholesterol are heritable, modifiable risk factors for coronary artery disease. To identify new loci and refine known loci influencing these lipids, we examined 188,577 individuals using genome-wide and custom genotyping arrays. We identify and annotate 157 loci associated with lipid levels at P < 5 × 10(-8), including 62 loci not previously associated with lipid levels in humans. Using dense genotyping in individuals of European, East Asian, South Asian and African ancestry, we narrow association signals in 12 loci. We find that loci associated with blood lipid levels are often associated with cardiovascular and metabolic traits, including coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, blood pressure, waist-hip ratio and body mass index. Our results demonstrate the value of using genetic data from individuals of diverse ancestry and provide insights into the biological mechanisms regulating blood lipids to guide future genetic, biological and therapeutic research.
Figures
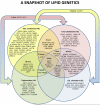
FIGURE 1. Overlap between loci associated with…
FIGURE 1. Overlap between loci associated with different lipid traits
This Venn Diagram illustrates the…
References
-
- Kannel WB, Dawber TR, Kagan A, Revotskie N, Stokes J., 3rd Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease--six year follow-up experience. The Framingham Study. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1961;55:33–50. - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP. Cholesterol and lipids in the risk of coronary artery disease--the Framingham Heart Study. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 1988;4(Suppl A):5A–10A. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CZB/4/672/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL109946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U950080926/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL069757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK082766/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U123092720/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901213/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 100891/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R00 HL094535/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/08/094/26019/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0801566/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

