Physiology and pathophysiology of SLC12A1/2 transporters
- PMID: 24097229
- PMCID: PMC3877717
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-013-1370-5
Physiology and pathophysiology of SLC12A1/2 transporters
Abstract
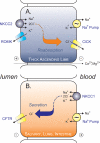
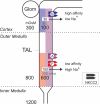
The electroneutral Na(+)-K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporters NKCC1 (encoded by the SLC12A2 gene) and NKCC2 (SLC12A1 gene) belong to the Na(+)-dependent subgroup of solute carrier 12 (SLC12) family of transporters. They mediate the electroneutral movement of Na(+) and K(+), tightly coupled to the movement of Cl(-) across cell membranes. As they use the energy of the ion gradients generated by the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase to transport Na(+), K(+), and Cl(-) from the outside to the inside of a cell, they are considered secondary active transport mechanisms. NKCC-mediated transport occurs in a 1Na(+), 1K(+), and 2Cl(-) ratio, although NKCC1 has been shown to sometimes mediate partial reactions. Both transporters are blocked by bumetanide and furosemide, drugs which are commonly used in clinical medicine. NKCC2 is the molecular target of loop diuretics as it is expressed on the apical membrane of thick ascending limb of Henle epithelial cells, where it mediates NaCl reabsorption. NKCC1, in contrast, is found on the basolateral membrane of Cl(-) secretory epithelial cells, as well as in a variety of non-epithelial cells, where it mediates cell volume regulation and participates in Cl(-) homeostasis. Following their molecular identification two decades ago, much has been learned about their biophysical properties, their mode of operation, their regulation by kinases and phosphatases, and their physiological relevance. However, despite this tremendous amount of new information, there are still so many gaps in our knowledge. This review summarizes information that constitutes consensus in the field, but it also discusses current points of controversy and highlights many unanswered questions.
Figures
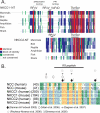
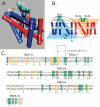
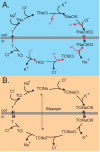
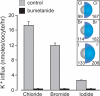
References
-
- Altamirano AA, Breitwieser GE, Russel JM. Vanadate and fluoride effects on Na-K-Cl cotransport in squid giant axon. Am J Physiol. 1988;254:C582–C586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

