Tn6188 - a novel transposon in Listeria monocytogenes responsible for tolerance to benzalkonium chloride
- PMID: 24098567
- PMCID: PMC3788773
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076835
Tn6188 - a novel transposon in Listeria monocytogenes responsible for tolerance to benzalkonium chloride
Abstract
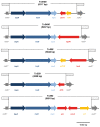
Controlling the food-borne pathogen Listeria (L.) monocytogenes is of great importance from a food safety perspective, and thus for human health. The consequences of failures in this regard have been exemplified by recent large listeriosis outbreaks in the USA and Europe. It is thus particularly notable that tolerance to quaternary ammonium compounds such as benzalkonium chloride (BC) has been observed in many L. monocytogenes strains. However, the molecular determinants and mechanisms of BC tolerance of L. monocytogenes are still largely unknown. Here we describe Tn6188, a novel transposon in L. monocytogenes conferring tolerance to BC. Tn6188 is related to Tn554 from Staphylococcus (S.) aureus and other Tn554-like transposons such as Tn558, Tn559 and Tn5406 found in various Firmicutes. Tn6188 comprises 5117 bp, is integrated chromosomally within the radC gene and consists of three transposase genes (tnpABC) as well as genes encoding a putative transcriptional regulator and QacH, a small multidrug resistance protein family (SMR) transporter putatively associated with export of BC that shows high amino acid identity to Smr/QacC from S. aureus and to EmrE from Escherichia coli. We screened 91 L. monocytogenes strains for the presence of Tn6188 by PCR and found Tn6188 in 10 of the analyzed strains. These isolates were from food and food processing environments and predominantly from serovar 1/2a. L. monocytogenes strains harboring Tn6188 had significantly higher BC minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) (28.5 ± 4.7 mg/l) than strains without Tn6188 (14 ± 3.2 mg/l). Using quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR we could show a significant increase in qacH expression in the presence of BC. QacH deletion mutants were generated in two L. monocytogenes strains and growth analysis revealed that ΔqacH strains had lower BC MICs than wildtype strains. In conclusion, our results provide evidence that Tn6188 is responsible for BC tolerance in various L. monocytogenes strains.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

