High-efficiency RNA cloning enables accurate quantification of miRNA expression by deep sequencing
- PMID: 24098942
- PMCID: PMC3983620
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-10-r109
High-efficiency RNA cloning enables accurate quantification of miRNA expression by deep sequencing
Abstract
Small RNA cloning and sequencing is uniquely positioned as a genome-wide approach to quantify miRNAs with single-nucleotide resolution. However, significant biases introduced by RNA ligation in current protocols lead to inaccurate miRNA quantification by 1000-fold. Here we report an RNA cloning method that achieves over 95% efficiency for both 5′ and 3′ ligations. It achieves accurate quantification of synthetic miRNAs with less than two-fold deviation from the anticipated value and over a dynamic range of four orders of magnitude. Taken together, this high-efficiency RNA cloning method permits accurate genome-wide miRNA profiling from total RNAs.
Figures
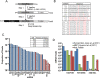
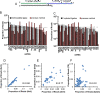
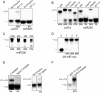
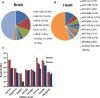
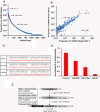
 indicates 3′ ligation product. The numbers at the bottom indicate the percentage of ligated species relative to the total. (B) 3′ ligation efficiencies were tested as in (A) with varying 3′ linkers and 10% w/v PEG8000. (C) 3′ ligation efficiency was enhanced by increasing the amount of NN linker used. The numbers at the top indicate fold molar excess of linker to substrate RNA. (D) A mixture of 29 synthetic miRNAs were radiolabeled and subjected to enhanced 3′ ligation conditions in the presence of 0.5 μg of total RNA obtained from mouse skin. The numbers at top indicate time in hours the reaction was carried out. (E) 5′ ligation efficiencies were assessed using gel-purified, radiolabeled, 3′ ligated, equimolar 29 synthetic miRNA mixtures with T4 RNL1 (left panel) at room temperature or with thermostable (TS) RNA ligase at 60°C (right panel) for 2 hours. The numbers at the bottom indicate the ligation efficiency, and a dash between two boxes indicates 5′ ligation product. (F) Optimized 5′ ligation reaction achieves 96% ligation efficiency.
indicates 3′ ligation product. The numbers at the bottom indicate the percentage of ligated species relative to the total. (B) 3′ ligation efficiencies were tested as in (A) with varying 3′ linkers and 10% w/v PEG8000. (C) 3′ ligation efficiency was enhanced by increasing the amount of NN linker used. The numbers at the top indicate fold molar excess of linker to substrate RNA. (D) A mixture of 29 synthetic miRNAs were radiolabeled and subjected to enhanced 3′ ligation conditions in the presence of 0.5 μg of total RNA obtained from mouse skin. The numbers at top indicate time in hours the reaction was carried out. (E) 5′ ligation efficiencies were assessed using gel-purified, radiolabeled, 3′ ligated, equimolar 29 synthetic miRNA mixtures with T4 RNL1 (left panel) at room temperature or with thermostable (TS) RNA ligase at 60°C (right panel) for 2 hours. The numbers at the bottom indicate the ligation efficiency, and a dash between two boxes indicates 5′ ligation product. (F) Optimized 5′ ligation reaction achieves 96% ligation efficiency.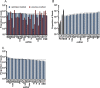

References
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;14:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005;14:769–773. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez AJ, Mishima Y, Rihel J, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Inoue K, Enright AJ, Schier AF. Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science. 2006;14:75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

