Drug-induced acute liver failure
- PMID: 24099019
- PMCID: PMC3838908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2013.07.001
Drug-induced acute liver failure
Abstract
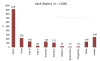
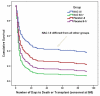
Although acute liver failure caused by drug-induced liver injury comprises a small fraction of overall drug-induced liver injury, these patients require high resource use and have relatively poor outcomes. Drug-induced liver injury caused by idiosyncrasy more often leads to death or transplantation than does acetaminophen acute liver failure, but the number of patients in each category receiving a graft is roughly the same. Efforts in the future to improve outcomes should focus on more effective treatments and better methods to identify those that might experience poor outcomes.
Keywords: Coagulopathy; Encephalopathy; Hepatocyte injury; Liver transplantation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ostapowicz GA, Fontana RJ, Schiodt FV, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:945–54. - PubMed
-
- Schiødt FV, Atillasoy E, Shakil O, et al. Etiology and outcome for 295 patients with acute liver failure in the United States. Liver Transpl Surg. 1999;5:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, et al. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010;376:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman HJ, Maddrey WC. Acetaminophen (paracetamol) hepatotoxicity with regular intake of alcohol: analysis of instances of therapeutic misadventure. Hepatology. 1995;22:767–73. - PubMed
-
- Wootton FT, Lee WM. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in the alcoholic. South Med J. 1990;83:1047–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical