The role of neutralizing antibodies in prevention of HIV-1 infection: what can we learn from the mother-to-child transmission context?
- PMID: 24099103
- PMCID: PMC3851888
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-103
The role of neutralizing antibodies in prevention of HIV-1 infection: what can we learn from the mother-to-child transmission context?
Abstract
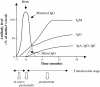
In most viral infections, protection through existing vaccines is linked to the presence of vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies (NAbs). However, more than 30 years after the identification of AIDS, the design of an immunogen able to induce antibodies that would neutralize the highly diverse HIV-1 variants remains one of the most puzzling challenges of the human microbiology. The role of antibodies in protection against HIV-1 can be studied in a natural situation that is the mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) context. Indeed, at least at the end of pregnancy, maternal antibodies of the IgG class are passively transferred to the fetus protecting the neonate from new infections during the first weeks or months of life. During the last few years, strong data, presented in this review, have suggested that some NAbs might confer protection toward neonatal HIV-1 infection. In cases of transmission, it has been shown that the viral population that is transmitted from the mother to the infant is usually homogeneous, genetically restricted and resistant to the maternal HIV-1-specific antibodies. Although the breath of neutralization was not associated with protection, it has not been excluded that NAbs toward specific HIV-1 strains might be associated with a lower rate of MTCT. A better identification of the antibody specificities that could mediate protection toward MTCT of HIV-1 would provide important insights into the antibody responses that would be useful for vaccine development. The most convincing data suggesting that NAbs might confer protection against HIV-1 infection have been obtained by experiments of passive immunization of newborn macaques with the first generation of human monoclonal broadly neutralizing antibodies (HuMoNAbs). However, these studies, which included only a few selected subtype B challenge viruses, provide data limited to protection against a very restricted number of isolates and therefore have limitations in addressing the hypervariability of HIV-1. The recent identification of highly potent second-generation cross-clade HuMoNAbs provides a new opportunity to evaluate the efficacy of passive immunization to prevent MTCT of HIV-1.
Figures


References
-
- Van Rompay KK, Berardi CJ, Dillard-Telm S, Tarara RP, Canfield DR, Valverde CR, Montefiori DC, Cole KS, Montelaro RC, Miller CJ, Marthas ML. Passive immunization of newborn rhesus macaques prevents oral simian immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:1247–1259. doi: 10.1086/515270. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baba TW, Liska V, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Vlasak J, Xu W, Ayehunie S, Cavacini LA, Posner MR, Katinger H, Stiegler G. et al. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat Med. 2000;6:200–206. doi: 10.1038/72309. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mascola JR, Stiegler G, VanCott TC, Katinger H, Carpenter CB, Hanson CE, Beary H, Hayes D, Frankel SS, Birx DL, Lewis MG. Protection of macaques against vaginal transmission of a pathogenic HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus by passive infusion of neutralizing antibodies. Nat Med. 2000;6:207–210. doi: 10.1038/72318. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

