Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin mediates rat pain-related responses induced by BmK I, a sodium channel-specific modulator
- PMID: 24099268
- PMCID: PMC3842742
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-50
Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin mediates rat pain-related responses induced by BmK I, a sodium channel-specific modulator
Abstract
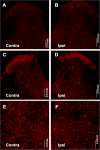
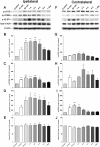
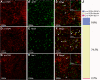
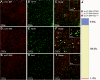
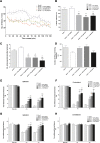
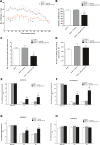
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is known to regulate cell proliferation and growth by controlling protein translation. Recently, it has been shown that mTOR signaling pathway is involved in long-term synaptic plasticity. However, the role of mTOR under different pain conditions is less clear. In this study, the spatiotemporal activation of mTOR that contributes to pain-related behaviors was investigated using a novel animal inflammatory pain model induced by BmK I, a sodium channel-specific modulator purified from scorpion venom. In this study, intraplantar injections of BmK I were found to induce the activation of mTOR, p70 ribosomal S6 protein kinase (p70 S6K) and eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) in rat L5-L6 spinal neurons. In the spinal cord, mTOR, p70 S6K and 4E-BP1 were observed to be activated in the ipsilateral and contralateral regions, peaking at 1-2 h and recovery at 24 h post-intraplantar (i.pl.) BmK I administration. In addition, intrathecal (i.t.) injection of rapamycin - a specific inhibitor of mTOR - was observed to result in the reduction of spontaneous pain responses and the attenuation of unilateral thermal and bilateral mechanical hypersensitivity elicited by BmK I. Thus, these results indicate that the mTOR signaling pathway is mobilized in the induction and maintenance of pain-activated hypersensitivity.
Figures




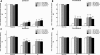
Similar articles
-
Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin contributes to pain nociception induced in rats by BmK I, a sodium channel-specific modulator.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Feb;30(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1377-0. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 24132796 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypes and peripheral mechanisms underlying inflammatory pain-related behaviors induced by BmK I, a modulator of sodium channels.Exp Neurol. 2010 Nov;226(1):159-72. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.08.018. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20736005
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin in spinal cord neurons mediates hypersensitivity induced by peripheral inflammation.Neuroscience. 2010 Sep 1;169(3):1392-402. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.05.067. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20538043 Free PMC article.
-
Functional up-regulation of Nav1.8 sodium channel on dorsal root ganglia neurons contributes to the induction of scorpion sting pain.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016 Feb;48(2):132-44. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv123. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016. PMID: 26764239
-
Revealing brain mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational regulation: Implications for chronic pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2018 Mar 21;4:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2018.03.002. eCollection 2018 Aug-Dec. Neurobiol Pain. 2018. PMID: 31194026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C-fiber recovery cycle supernormality depends on ion concentration and ion channel permeability.Biophys J. 2015 Mar 10;108(5):1057-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.12.034. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25762318 Free PMC article.
-
Role of fragile X mental retardation protein in chronic pain.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920928619. doi: 10.1177/1744806920928619. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 32496847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equivalent intraperitoneal doses of ibuprofen supplemented in drinking water or in diet: a behavioral and biochemical assay using antinociceptive and thromboxane inhibitory dose-response curves in mice.PeerJ. 2016 Jul 19;4:e2239. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2239. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27547547 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of P2X7 Receptors Contributes to Spinal Microglial Activation and the Development of Pain Induced by BmK-I.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Aug;35(4):624-636. doi: 10.1007/s12264-019-00345-0. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 30820829 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of rapamycin on status epilepticus induced hippocampal pathology and weight gain.Exp Neurol. 2016 Jun;280:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26995324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balozet L. In: Venomous Animal and Their Venoms. Bucherl W, Buckley EE, editor. Vol. 3. New York: Academic Press; 1971. Scorpionism in the old world; pp. 349–371.
-
- Ji YH, Mansuelle P, Xu K, Granier C, Kopeyan C, Terakawa S, Rochat H. Amino acid sequence of an excitatory insect-selective toxin (BmK IT) from venom of the scorpion Buthus martensi Karsch. Sci China B. 1994;37:42–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

