Structure of the polypeptide crotamine from the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus
- PMID: 24100315
- PMCID: PMC3792641
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444913018003
Structure of the polypeptide crotamine from the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus
Abstract
The crystal structure of the myotoxic, cell-penetrating, basic polypeptide crotamine isolated from the venom of Crotalus durissus terrificus has been determined by single-wavelength anomalous dispersion techniques and refined at 1.7 Å resolution. The structure reveals distinct cationic and hydrophobic surface regions that are located on opposite sides of the molecule. This surface-charge distribution indicates its possible mode of interaction with negatively charged phospholipids and other molecular targets to account for its diverse pharmacological activities. Although the sequence identity between crotamine and human β-defensins is low, the three-dimensional structures of these functionally related peptides are similar. Since crotamine is a leading member of a large family of myotoxic peptides, its structure will provide a basis for the design of novel cell-penetrating molecules.
Keywords: crotamine; natural cell-penetrating polypeptides; snake venoms.
Figures
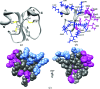


Similar articles
-
Snake venomics of the Central American rattlesnake Crotalus simus and the South American Crotalus durissus complex points to neurotoxicity as an adaptive paedomorphic trend along Crotalus dispersal in South America.J Proteome Res. 2010 Jan;9(1):528-44. doi: 10.1021/pr9008749. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 19863078
-
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of crotamine, a myotoxic polypeptide from the Brazilian snake Crotalus durissus terrificus.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Sep 1;68(Pt 9):1052-4. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112032721. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 22949192 Free PMC article.
-
Crotamine, a small basic polypeptide myotoxin from rattlesnake venom with cell-penetrating properties.Curr Pharm Des. 2011 Dec;17(38):4351-61. doi: 10.2174/138161211798999429. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 22204433 Review.
-
Snake venomics and antivenomics of Crotalus durissus subspecies from Brazil: assessment of geographic variation and its implication on snakebite management.J Proteomics. 2010 Aug 5;73(9):1758-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 11. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20542151
-
New view on crotamine, a small basic polypeptide myotoxin from South American rattlesnake venom.Toxicon. 2005 Sep 15;46(4):363-70. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.06.009. Toxicon. 2005. PMID: 16115660 Review.
Cited by
-
Snake Venom Peptides: Tools of Biodiscovery.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 14;10(11):474. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110474. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30441876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crotamine derived from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom combined with drugs increases in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Aug 6;206(9):368. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04096-z. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39107625
-
Snake Venom: A Promising Source of Neurotoxins Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Dec 25;16(1):12. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010012. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38251229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hitchhiking with Nature: Snake Venom Peptides to Fight Cancer and Superbugs.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 15;12(4):255. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040255. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemistry of snake venom and its medicinal potential.Nat Rev Chem. 2022;6(7):451-469. doi: 10.1038/s41570-022-00393-7. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Nat Rev Chem. 2022. PMID: 35702592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Boni-Mitake, M., Costa, H., Spencer, P. J., Vassilieff, V. S. & Rogero, J. R. (2001). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 34, 1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Bontems, F., Gilquin, B., Roumestand, C., Ménez, A. & Toma, F. (1992). Biochemistry, 31, 7756–7764. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho, A. de O. & Gomes, V. M. (2009). Peptides, 30, 1007–1020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

