Structures of the Porphyromonas gingivalis OxyR regulatory domain explain differences in expression of the OxyR regulon in Escherichia coli and P. gingivalis
- PMID: 24100327
- PMCID: PMC3792645
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444913019471
Structures of the Porphyromonas gingivalis OxyR regulatory domain explain differences in expression of the OxyR regulon in Escherichia coli and P. gingivalis
Abstract
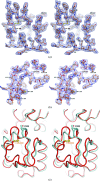
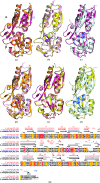
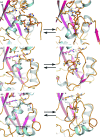
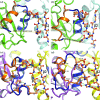
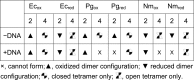
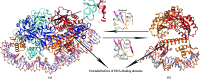
OxyR transcriptionally regulates Escherichia coli oxidative stress response genes through a reversibly reducible cysteine disulfide biosensor of cellular redox status. Structural changes induced by redox changes in these cysteines are conformationally transmitted to the dimer subunit interfaces, which alters dimer and tetramer interactions with DNA. In contrast to E. coli OxyR regulatory-domain structures, crystal structures of Porphyromonas gingivalis OxyR regulatory domains show minimal differences in dimer configuration on changes in cysteine disulfide redox status. This locked configuration of the P. gingivalis OxyR regulatory-domain dimer closely resembles the oxidized (activating) form of the E. coli OxyR regulatory-domain dimer. It correlates with the observed constitutive activation of some oxidative stress genes in P. gingivalis and is attributable to a single amino-acid insertion in P. gingivalis OxyR relative to E. coli OxyR. Modelling of full-length P. gingivalis, E. coli and Neisseria meningitidis OxyR-DNA complexes predicts different modes of DNA binding for the reduced and oxidized forms of each.
Keywords: OxyR; Porphyromonas gingivalis; regulatory domain.
Figures
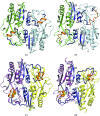
Similar articles
-
Structural basis of the redox switch in the OxyR transcription factor.Cell. 2001 Apr 6;105(1):103-13. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00300-2. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11301006
-
The structure of a reduced form of OxyR from Neisseria meningitidis.BMC Struct Biol. 2010 May 17;10:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-10-10. BMC Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20478059 Free PMC article.
-
The redox-sensitive transcriptional activator OxyR regulates the peroxide response regulon in the obligate anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis.J Bacteriol. 2000 Sep;182(18):5059-69. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.18.5059-5069.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10960088 Free PMC article.
-
The OxyR regulon.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990 Oct;58(3):157-61. doi: 10.1007/BF00548927. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990. PMID: 2256675 Review.
-
Redox-operated genetic switches: the SoxR and OxyR transcription factors.Trends Biotechnol. 2001 Mar;19(3):109-14. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(00)01542-0. Trends Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11179804 Review.
Cited by
-
Tolerance to oxidative stress is required for maximal xylem colonization by the xylem-limited bacterial phytopathogen, Xylella fastidiosa.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Sep;18(7):990-1000. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12456. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27377476 Free PMC article.
-
Structural details of the OxyR peroxide-sensing mechanism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 19;112(20):6443-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424495112. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25931525 Free PMC article.
-
How Bacterial Redox Sensors Transmit Redox Signals via Structural Changes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;10(4):502. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040502. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural snapshots of OxyR reveal the peroxidatic mechanism of H2O2 sensing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 11;115(50):E11623-E11632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1807954115. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30463959 Free PMC article.
-
Insertional Inactivation of Prevotella intermedia OxyR Results in Reduced Survival with Oxidative Stress and in the Presence of Host Cells.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 7;9(3):551. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030551. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33800047 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

