Approaches to the synthesis of a novel, anti-HIV active integrase inhibitor
- PMID: 24100441
- PMCID: PMC3846259
- DOI: 10.1039/c3ob41728j
Approaches to the synthesis of a novel, anti-HIV active integrase inhibitor
Abstract
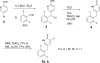
The novel HIV-1 integrase inhibitor 1, discovered in our laboratory, exhibits potent anti-HIV activity against a diverse set of HIV-1 isolates and also against HIV-2 and SIV. In addition, this compound displays low cellular cytotoxicity and possesses a favorable in vitro drug interaction profile with respect to isozymes of cytochrome P450 (CYP) and uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). However, the total synthesis of this significant HIV integrase inhibitor has not been reported. This contribution describes an optimized, reproducible, multi-step, synthetic route to inhibitor 1. The yield for the separate steps averaged about 80%. The methodologies utilized in the synthesis were, among others, a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction, a crossed-Claisen condensation, and a hydrazino amide synthesis step. Successful alternative synthetic methodologies for some of the steps are also described.
Figures


References
-
- Dye C, Williams BG. Science. 2010;328:856–861. - PubMed
-
- Trono D, Van Lint C, Rouzioux C, Verdin E, Barre-Sinoussi F, Chun TW, Chomont N. Science. 2010;329:174–180. - PubMed
-
- Josephson F. J. Intern. Med. 2010;268:530–539. - PubMed
-
- Kiang TKL, Ensom MHH, Chang TKH. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2005;106:97–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

