Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of D-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase isolated from Delftia sp. HT23
- PMID: 24100565
- PMCID: PMC3792673
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309113023956
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of D-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase isolated from Delftia sp. HT23
Abstract
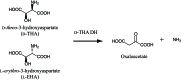
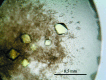
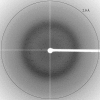
D-threo-3-Hydroxyaspartate dehydratase (D-THA DH) isolated from the soil bacterium Delftia sp. HT23 is a novel enzyme consisting of 380 amino-acid residues which catalyzes the conversion of D-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate to oxaloacetate and ammonia. D-THA DH also catalyzes the dehydration of L-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate, L-erythro-3-hydroxyaspartate and D-serine. The amino-acid sequence of D-THA DH shows significant similarity to that of two eukaryotic D-serine dehydratases derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and chicken kidney. D-THA DH is classified into the fold-type III group of pyridoxal enzymes and is the first example of a fold-type III dehydratase derived from a prokaryote. Overexpression of recombinant D-THA DH was carried out using a Rhodococcus erythropolis expression system and the obtained protein was subsequently purified and crystallized. The crystals of D-THA DH belonged to space group I4₁22, with unit-cell parameters a=b=157.3, c=157.9 Å. Single-wavelength anomalous diffraction data were collected to a resolution of 2.0 Å using synchrotron radiation at the wavelength of the Br K absorption edge.
Keywords: Br-SAD; Delftia sp. HT23; alanine racemase; d-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase; pyridoxal 5′-phosphate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Purification, characterization and amino acid sequence of a novel enzyme, D-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase, from Delftia sp. HT23.J Biochem. 2010 Dec;148(6):705-12. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvq106. Epub 2010 Sep 14. J Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20843822
-
Structural insights into the substrate stereospecificity of D-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase from Delftia sp. HT23: a useful enzyme for the synthesis of optically pure L-threo- and D-erythro-3-hydroxyaspartate.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;99(17):7137-50. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6479-3. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25715785
-
Gene cloning and expression of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent L-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase from Pseudomonas sp. T62, and characterization of the recombinant enzyme.J Biochem. 2009 May;145(5):661-8. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvp023. Epub 2009 Feb 4. J Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19193709
-
Isolation and amino acid sequence of a dehydratase acting on d-erythro-3-hydroxyaspartate from Pseudomonas sp. N99, and its application in the production of optically active 3-hydroxyaspartate.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Jun;81(6):1156-1164. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1295804. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28290777
-
Purification and characterization of a novel enzyme, L-threo-3-hydroxyaspartate dehydratase, from Pseudomonas sp. T62.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999 Oct 1;179(1):147-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb08720.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10481099
References
-
- Balcar, V. J., Johnston, G. A. & Twitchin, B. (1977). J. Neurochem. 28, 1145–1146. - PubMed
-
- Dauter, Z., Dauter, M. & Rajashankar, K. R. (2000). Acta Cryst. D56, 232–237. - PubMed
-
- Eliot, A. C. & Kirsch, J. F. (2004). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 383–415. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs, R. G. & Morris, J. G. (1964). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 85, 501–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

