Expression, purification and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of Arf1-GDP in complex with dimeric p23 peptide
- PMID: 24100571
- PMCID: PMC3792679
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309113024330
Expression, purification and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of Arf1-GDP in complex with dimeric p23 peptide
Abstract
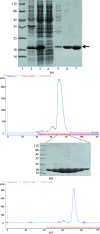
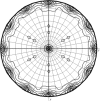
Arf1 is a member of the Ras superfamily and is involved in COPI vesicle formation. Arf1-GDP can interact with dimeric p23. Here, human Arf1 (residues 18-181) was cloned, expressed and purified in Escherichia coli. For crystallization, Arf1-GDP was mixed with dimeric p23 peptide in a 1:5 molar ratio. Crystals were obtained which diffracted to 2.7 Å resolution. The crystals belonged to space group P6₁22, with unit-cell parameters a=b=80.6, c=336.0 Å, α=β=90, γ=120°. The asymmetric unit of the crystals contained two molecules, with a Matthews coefficient of 3.2 Å3 Da(-1) and a solvent content of 61.9%.
Keywords: Arf1; COPI; dimer; p23.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recruitment to Golgi membranes of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 is mediated by the cytoplasmic domain of p23.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6751-60. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6751. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11726511 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational states of the small G protein Arf-1 in complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange factor ARNO-Sec7.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17004-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312780200. Epub 2004 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14739276
-
Crystal structure of ARF1*Sec7 complexed with Brefeldin A and its implications for the guanine nucleotide exchange mechanism.Mol Cell. 2003 Dec;12(6):1403-11. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00475-1. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14690595
-
Binding site of brefeldin A at the interface between the small G protein ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) and the nucleotide-exchange factor Sec7 domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 29;97(18):9913-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.170290597. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10954741 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, purification, and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the complex of G(alphai3)-RGS5 from human with GDP/Mg2+)/AlF4-.Protein Pept Lett. 2006;13(9):945-9. doi: 10.2174/092986606778256225. Protein Pept Lett. 2006. PMID: 17100651
Cited by
-
Strategies for Optimizing the Production of Proteins and Peptides with Multiple Disulfide Bonds.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;9(9):541. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090541. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32858882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

