Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape
- PMID: 24101477
- PMCID: PMC3808615
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1308887110
Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape
Abstract
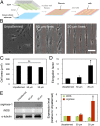
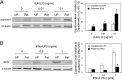
Phenotypic polarization of macrophages is regulated by a milieu of cues in the local tissue microenvironment. Although much is known about how soluble factors influence macrophage polarization, relatively little is known about how physical cues present in the extracellular environment might modulate proinflammatory (M1) vs. prohealing (M2) activation. Specifically, the role of cell shape has not been explored, even though it has been observed that macrophages adopt different geometries in vivo. We and others observed that macrophages polarized toward different phenotypes in vitro exhibit dramatic changes in cell shape: M2 cells exhibit an elongated shape compared with M1 cells. Using a micropatterning approach to control macrophage cell shape directly, we demonstrate here that elongation itself, without exogenous cytokines, leads to the expression of M2 phenotype markers and reduces the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, elongation enhances the effects of M2-inducing cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 and protects cells from M1-inducing stimuli LPS and IFN-γ. In addition shape- but not cytokine-induced polarization is abrogated when actin and actin/myosin contractility are inhibited by pharmacological agents, suggesting a role for the cytoskeleton in the control of macrophage polarization by cell geometry. Our studies demonstrate that alterations in cell shape associated with changes in ECM architecture may provide integral cues to modulate macrophage phenotype polarization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lucas T, et al. Differential roles of macrophages in diverse phases of skin repair. J Immunol. 2010;184(7):3964–3977. - PubMed
-
- Daley JM, et al. Modulation of macrophage phenotype by soluble product(s) released from neutrophils. J Immunol. 2005;174(4):2265–2272. - PubMed
-
- Van Goethem E, Poincloux R, Gauffre F, Maridonneau-Parini I, Le Cabec V. Matrix architecture dictates three-dimensional migration modes of human macrophages: Differential involvement of proteases and podosome-like structures. J Immunol. 2010;184(2):1049–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

