Expanded therapeutic potential in activity space of next-generation 5-nitroimidazole antimicrobials with broad structural diversity
- PMID: 24101497
- PMCID: PMC3808650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1302664110
Expanded therapeutic potential in activity space of next-generation 5-nitroimidazole antimicrobials with broad structural diversity
Abstract
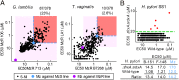
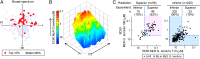
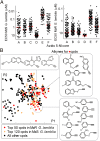
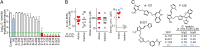
Metronidazole and other 5-nitroimidazoles (5-NI) are among the most effective antimicrobials available against many important anaerobic pathogens, but evolving resistance is threatening their long-term clinical utility. The common 5-NIs were developed decades ago, yet little 5-NI drug development has since taken place, leaving the true potential of this important drug class unexplored. Here we report on a unique approach to the modular synthesis of diversified 5-NIs for broad exploration of their antimicrobial potential. Many of the more than 650 synthesized compounds, carrying structurally diverse functional groups, have vastly improved activity against a range of microbes, including the pathogenic protozoa Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis, and the bacterial pathogens Helicobacter pylori, Clostridium difficile, and Bacteroides fragilis. Furthermore, they can overcome different forms of drug resistance, and are active and nontoxic in animal infection models. These findings provide impetus to the development of structurally diverse, next-generation 5-NI drugs as agents in the antimicrobial armamentarium, thus ensuring their future viability as primary therapeutic agents against many clinically important infections.
Keywords: antibiotics; infectious diseases; medicinal chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nitroimidazole carboxamides as antiparasitic agents targeting Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Sep 14;120:353-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.04.064. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27236016 Free PMC article.
-
5-Nitroimidazole drugs effective against metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis and Giardia duodenalis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jan;50(1):344-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.344-347.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16377707 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and electrochemistry of 2-ethenyl and 2-ethanyl derivatives of 5-nitroimidazole and antimicrobial activity against Giardia lamblia.J Med Chem. 2009 Jul 9;52(13):4038-53. doi: 10.1021/jm900356n. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19480409 Free PMC article.
-
Drug targets and mechanisms of resistance in the anaerobic protozoa.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001 Jan;14(1):150-64. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.1.150-164.2001. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11148007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitroimidazoles: Molecular Fireworks That Combat a Broad Spectrum of Infectious Diseases.J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 28;60(18):7636-7657. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00143. Epub 2017 May 22. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28463485 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Benzopyrrolizidines as Promising Antigiardiasic Agents.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 12;11:828100. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.828100. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35096662 Free PMC article.
-
In Situ Reactivity of Electrochemically Generated Nitro Radical Anion on Tinidazole and Its Monomeric and Dimeric CuII Complexes on Model Biological Targets with Relative Manifestation of Preventing Bacterial Biofilm Formation.ACS Omega. 2022 Mar 1;7(10):8268-8280. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04822. eCollection 2022 Mar 15. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35309450 Free PMC article.
-
Composite thermoresponsive hydrogel with auranofin-loaded nanoparticles for topical treatment of vaginal trichomonad infection.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2019 Dec;2(12):1900157. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201900157. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 32377561 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin inactivates Trichomonas vaginalis thioredoxin reductase and is effective against trichomonads in vitro and in vivo.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016 Dec;48(6):690-694. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.09.020. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. PMID: 27839893 Free PMC article.
-
Amidinoquinoxaline N-oxides: synthesis and activity against anaerobic bacteria.RSC Adv. 2023 Sep 13;13(39):27391-27402. doi: 10.1039/d3ra01184d. eCollection 2023 Sep 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37711381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brook I. Antimicrobial treatment of anaerobic infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011;12(11):1691–1707. - PubMed
-
- Edwards DI. Nitroimidazole drugs—Action and resistance mechanisms. I. Mechanisms of action. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993;31(1):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Löfmark S, Edlund C, Nord CE. Metronidazole is still the drug of choice for treatment of anaerobic infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(Suppl 1):S16–S23. - PubMed

