Serum deprivation inhibits the transcriptional co-activator YAP and cell growth via phosphorylation of the 130-kDa isoform of Angiomotin by the LATS1/2 protein kinases
- PMID: 24101513
- PMCID: PMC3808603
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1308236110
Serum deprivation inhibits the transcriptional co-activator YAP and cell growth via phosphorylation of the 130-kDa isoform of Angiomotin by the LATS1/2 protein kinases
Abstract
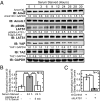
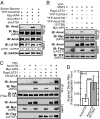
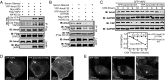
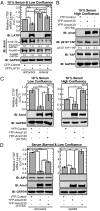
Large tumor suppressor (LATS)1/2 protein kinases transmit Hippo signaling in response to intercellular contacts and serum levels to limit cell growth via the inhibition of Yes-associated protein (YAP). Here low serum and high LATS1 activity are found to enhance the levels of the 130-kDa isoform of angiomotin (Amot130) through phosphorylation by LATS1/2 at serine 175, which then forms a binding site for 14-3-3. Such phosphorylation, in turn, enables the ubiquitin ligase atrophin-1 interacting protein (AIP)4 to bind, ubiquitinate, and stabilize Amot130. Consistently, the Amot130 (S175A) mutant, which lacks LATS phosphorylation, bound AIP4 poorly under all conditions and showed reduced stability. Amot130 and AIP4 also promoted the ubiquitination and degradation of YAP in response to serum starvation, unlike Amot130 (S175A). Moreover, silencing Amot130 expression blocked LATS1 from inhibiting the expression of connective tissue growth factor, a YAP-regulated gene. Concordant with phosphorylated Amot130 specifically mediating these effects, wild-type Amot130 selectively induced YAP phosphorylation and reduced transcription of connective tissue growth factor in an AIP4-dependent manner versus Amot130 (S175A). Further, Amot130 but not Amot130 (S175A) strongly inhibited the growth of MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells. The dominant-negative effects of Amot130 (S175A) on YAP signaling also support that phosphorylated Amot130 transduces Hippo signaling. Likewise, Amot130 expression provoked premature growth arrest during mammary cell acini formation, whereas Amot130 (S175A)-expressing cells formed enlarged and poorly differentiated acini. Taken together, the phosphorylation of Amot130 by LATS is found to be a key feature that enables it to inhibit YAP-dependent signaling and cell growth.
Keywords: Itch; breast cancer; growth control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Miller E, et al. Identification of serum-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate as a small molecule regulator of YAP. Chem Biol. 2012;19(8):955–962. - PubMed
-
- Oka T, Mazack V, Sudol M. Mst2 and Lats kinases regulate apoptotic function of Yes kinase-associated protein (YAP) J Biol Chem. 2008;283(41):27534–27546. - PubMed
-
- Pan D. Hippo signaling in organ size control. Genes Dev. 2007;21(8):886–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

