Granzyme B degradation by autophagy decreases tumor cell susceptibility to natural killer-mediated lysis under hypoxia
- PMID: 24101526
- PMCID: PMC3808626
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304790110
Granzyme B degradation by autophagy decreases tumor cell susceptibility to natural killer-mediated lysis under hypoxia
Abstract
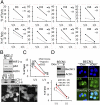
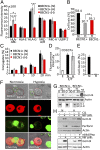
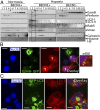
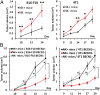
Recent studies demonstrated that autophagy is an important regulator of innate immune response. However, the mechanism by which autophagy regulates natural killer (NK) cell-mediated antitumor immune responses remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that hypoxia impairs breast cancer cell susceptibility to NK-mediated lysis in vitro via the activation of autophagy. This impairment was not related to a defect in target cell recognition by NK cells but to the degradation of NK-derived granzyme B in autophagosomes of hypoxic cells. Inhibition of autophagy by targeting beclin1 (BECN1) restored granzyme B levels in hypoxic cells in vitro and induced tumor regression in vivo by facilitating NK-mediated tumor cell killing. Together, our data highlight autophagy as a mechanism underlying the resistance of hypoxic tumor cells to NK-mediated lysis. The work presented here provides a cutting-edge advance in our understanding of the mechanism by which hypoxia-induced autophagy impairs NK-mediated lysis in vitro and paves the way for the formulation of more effective NK cell-based antitumor therapies.
Keywords: breast adenocarcinoma; hypoxic tumor microenvironment; immunotherapy; innate immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zitvogel L, Tesniere A, Kroemer G. Cancer despite immunosurveillance: immunoselection and immunosubversion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(10):715–727. - PubMed
-
- Smyth MJ, Hayakawa Y, Takeda K, Yagita H. New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(11):850–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

