Asymptomatic HLA-A*02:01-restricted epitopes from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B preferentially recall polyfunctional CD8+ T cells from seropositive asymptomatic individuals and protect HLA transgenic mice against ocular herpes
- PMID: 24101547
- PMCID: PMC4057607
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301415
Asymptomatic HLA-A*02:01-restricted epitopes from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B preferentially recall polyfunctional CD8+ T cells from seropositive asymptomatic individuals and protect HLA transgenic mice against ocular herpes
Abstract
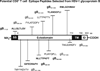
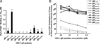
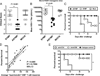
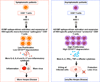
Evidence from C57BL/6 mice suggests that CD8(+) T cells, specific to the immunodominant HSV-1 glycoprotein B (gB) H-2(b)-restricted epitope (gB498-505), protect against ocular herpes infection and disease. However, the possible role of CD8(+) T cells, specific to HLA-restricted gB epitopes, in protective immunity seen in HSV-1-seropositive asymptomatic (ASYMP) healthy individuals (who have never had clinical herpes) remains to be determined. In this study, we used multiple prediction algorithms to identify 10 potential HLA-A*02:01-restricted CD8(+) T cell epitopes from the HSV-1 gB amino acid sequence. Six of these epitopes exhibited high-affinity binding to HLA-A*02:01 molecules. In 10 sequentially studied HLA-A*02:01-positive, HSV-1-seropositive ASYMP individuals, the most frequent, robust, and polyfunctional CD8(+) T cell responses, as assessed by a combination of tetramer, IFN-γ-ELISPOT, CFSE proliferation, CD107a/b cytotoxic degranulation, and multiplex cytokine assays, were directed mainly against epitopes gB342-350 and gB561-569. In contrast, in 10 HLA-A*02:01-positive, HSV-1-seropositive symptomatic (SYMP) individuals (with a history of numerous episodes of recurrent clinical herpes disease) frequent, but less robust, CD8(+) T cell responses were directed mainly against nonoverlapping epitopes (gB183-191 and gB441-449). ASYMP individuals had a significantly higher proportion of HSV-gB-specific CD8(+) T cells expressing CD107a/b degranulation marker and producing effector cytokines IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α than did SYMP individuals. Moreover, immunization of a novel herpes-susceptible HLA-A*02:01 transgenic mouse model with ASYMP epitopes, but not with SYMP epitopes, induced strong CD8(+) T cell-dependent protective immunity against ocular herpes infection and disease. These findings should guide the development of a safe and effective T cell-based herpes vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang X, Dervillez X, Chentoufi AA, Badakhshan T, Bettahi I, BenMohamed L. Targeting the genital tract mucosa with a lipopeptide/recombinant adenovirus prime/boost vaccine induces potent and long-lasting CD8+ T cell immunity against herpes: importance of MyD88. J. Immunol. 2012;189:4496–4509. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chentoufi AA, Dasgupta G, Christensen ND, Hu J, Choudhury ZS, Azeem A, Jester JV, Nesburn AB, Wechsler SL, BenMohamed L. A novel HLA (HLA-A*0201) transgenic rabbit model for preclinical evaluation of human CD8+ T cell epitope-based vaccines against ocular herpes. J. Immunol. 2010;184:2561–2571. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chentoufi AA, Zhang X, Lamberth K, Dasgupta G, Bettahi I, Nguyen A, Wu M, Zhu X, Mohebbi A, Buus S, et al. HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes identified from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D. J. Immunol. 2008;180:426–437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

