In vivo transfection of manganese superoxide dismutase gene or nuclear factor κB shRNA in nodose ganglia improves aortic baroreceptor function in heart failure rats
- PMID: 24101667
- PMCID: PMC3893036
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02057
In vivo transfection of manganese superoxide dismutase gene or nuclear factor κB shRNA in nodose ganglia improves aortic baroreceptor function in heart failure rats
Abstract
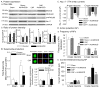
Arterial baroreflex sensitivity is attenuated in chronic heart failure (CHF) state, which is associated with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in patients with CHF. Our previous study showed that CHF-induced sodium channel dysfunction in the baroreceptor neurons was involved in the blunted baroreflex sensitivity in CHF rats. Mitochondria-derived superoxide overproduction decreased expression and activation of the sodium channels in the baroreceptor neurons from CHF rats. However, the molecular mechanisms responsible for the sodium channel dysfunction in the baroreceptor neurons from CHF rats remain unknown. We tested the involvement of nuclear factor κB (NFκB) in the sodium channel dysfunction and evaluated the effects of in vivo transfection of manganese superoxide dismutase gene and NFκB shRNA on the baroreflex function in CHF rats. CHF was developed at 6 to 8 weeks after left coronary artery ligation in adult rats. Western blot and chromatin immunoprecipitation data showed that phosphorylated NFκB p65 and ability of NFκB p65 binding to the sodium channel promoter were increased in the nodose ganglia from CHF rats. In vivo transfection of adenoviral manganese superoxide dismutase gene or lentiviral NFκB p65 shRNA into the nodose ganglia partially reversed CHF-reduced sodium channel expression and cell excitability in the baroreceptor neurons and improved CHF-blunted arterial baroreflex sensitivity. Additionally, transfection of adenoviral manganese superoxide dismutase also inhibited the augmentation of phosphorylated NFκB p65 in the nodose neurons from CHF rats. The present study suggests that superoxide-NFκB signaling contributes to CHF-induced baroreceptor dysfunction and resultant impairment of baroreflex function.
Keywords: baroreflex; heart failure; pressoreceptors; sodium channels; superoxides.
Figures
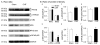
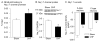


Similar articles
-
Mitochondria-derived superoxide and voltage-gated sodium channels in baroreceptor neurons from chronic heart-failure rats.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Jan;107(2):591-602. doi: 10.1152/jn.00754.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22072507 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of angiotensin II on voltage-gated sodium currents in aortic baroreceptor neurons and arterial baroreflex sensitivity in heart failure rats.J Hypertens. 2015 Jul;33(7):1401-10. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000563. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25827427 Free PMC article.
-
Altered ENaC is Associated With Aortic Baroreceptor Dysfunction in Chronic Heart Failure.Am J Hypertens. 2016 May;29(5):582-9. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpv141. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Am J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26297031 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-superoxide-NFκB signaling and aortic baroreceptor dysfunction in chronic heart failure.Front Neurosci. 2015 Oct 16;9:382. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00382. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26528122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Arterial Baroreceptor Remodeling in Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Feb;35(1):98-112. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0274-y. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 30146675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Hypertensive Action of Fenofibrate via UCP2 Upregulation Mediated by PPAR Activation in Baroreflex Afferent Pathway.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Feb;35(1):15-24. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0271-1. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 30173356 Free PMC article.
-
Direct activation of tachykinin receptors within baroreflex afferent pathway and neurocontrol of blood pressure regulation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Jan;25(1):123-135. doi: 10.1111/cns.12993. Epub 2018 Jun 13. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 29900692 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson-like early autonomic dysfunction induced by vagal application of DOPAL in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 May;27(5):540-551. doi: 10.1111/cns.13589. Epub 2021 Jan 21. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 33475253 Free PMC article.
-
Altered leptin signaling and attenuated cardiac vagal activity in rats with type 2 diabetes.Front Physiol. 2025 Feb 26;16:1547901. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1547901. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40078371 Free PMC article.
-
Stellate Ganglia and Cardiac Sympathetic Overactivation in Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 1;23(21):13311. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113311. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruttanaumpawan P, Gilman MP, Usui K, Floras JS, Bradley TD. Sustained effect of continuous positive airway pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in congestive heart failure patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Hypertens. 2008;26:1163–1168. - PubMed
-
- Floras JS. Clinical aspects of sympathetic activation and parasympathetic withdrawal in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22:72A–84A. - PubMed
-
- Pinna GD, Maestri R, Capomolla S, Febo O, Robbi E, Cobelli F, La Rovere MT. Applicability and clinical relevance of the transfer function method in the assessment of baroreflex sensitivity in heart failure patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:1314–1321. - PubMed
-
- Creager MA, Creager SJ. Arterial baroreflex regulation of blood pressure in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;23:401–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

