Molecular mechanisms of renal and extrarenal manifestations caused by inactivation of the electrogenic Na(+)-HCO3 (-) cotransporter NBCe1
- PMID: 24101904
- PMCID: PMC3787273
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00270
Molecular mechanisms of renal and extrarenal manifestations caused by inactivation of the electrogenic Na(+)-HCO3 (-) cotransporter NBCe1
Abstract
The electrogenic Na(+)-HCO3 (-) cotransporter NBCe1 plays an essential role in bicarbonate absorption from renal proximal tubules, but also mediates the other biological processes in extrarenal tissues such as bicarbonate secretion from pancreatic ducts, maintenance of tissue homeostasis in eye, enamel maturation in teeth, or local pH regulation in synapses. Homozygous mutation in NBCe1 cause proximal renal tubular acidosis (pRTA) associated with extrarenal manifestations such as short stature, ocular abnormalities, enamel abnormalities, and migraine. Functional analyses of NBCe1 mutants using different expression systems suggest that at least a 50% reduction of the transport activity may be required to induce severe pRTA. In addition to functional impairments, some NBCe1 mutants show trafficking defects. Some of the pRTA-related NBCe1 mutants showing the cytoplasmic retention have been shown to exert a dominant negative effect through hetero-oligomer complexes with wild-type NBCe1 that may explain the occurrence of extrarenal manifestations in the heterozygous carries of NBCe1 mutations. Both NBCe1 knockout (KO) and W516X knockin (KI) mice showed very severe pRTA and reproduced most of the clinical manifestations observed in human pRTA patients. Functional analysis on isolated renal proximal tubules from W516X KI mice directly confirmed the indispensable role of NBCe1 in bicarbonate absorption from this nephron segment. In this review, we will focus on the molecular mechanisms underling the renal and extrarenal manifestations caused by NBCe1 inactivation.
Keywords: NBCe1; dominant negative effect; enamel abnormalities; migraine; ocular abnormalities; pRTA; short stature.
Figures
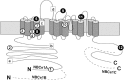
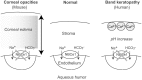
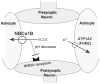
Similar articles
-
A novel mutant Na+ /HCO3- cotransporter NBCe1 in a case of compound-heterozygous inheritance of proximal renal tubular acidosis.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;594(21):6267-6286. doi: 10.1113/JP272252. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27338124 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of dominant negative effect of L522P mutation in the electrogenic Na⁺-HCO₃⁻ cotransporter NBCe1.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Sep;465(9):1281-91. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1277-1. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23559100
-
Extrarenal Signs of Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis Persist in Nonacidemic Nbce1b/c-Null Mice.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Jun;30(6):979-989. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018050545. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31040187 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal renal tubular acidosis mediated by mutations in NBCe1-A: unraveling the transporter's structure-functional properties.Front Physiol. 2013 Dec 19;4:350. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00350. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24391589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of proximal renal tubular acidosis.J Nephrol. 2002 Mar-Apr;15 Suppl 5:S135-41. J Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12027212 Review.
Cited by
-
SLC4A4 compound heterozygous mutations in exon-intron boundary regions presenting with severe proximal renal tubular acidosis and extrarenal symptoms coexisting with Turner's syndrome: a case report.BMC Med Genet. 2018 Jun 18;19(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0612-y. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29914390 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between disulfide bonding and N-glycosylation defines SLC4 Na+-coupled transporter extracellular topography.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 27;290(9):5391-404. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619320. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25568315 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mutant Na+ /HCO3- cotransporter NBCe1 in a case of compound-heterozygous inheritance of proximal renal tubular acidosis.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;594(21):6267-6286. doi: 10.1113/JP272252. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27338124 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of renal proximal tubule transport in acid/base balance and blood pressure regulation.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:504808. doi: 10.1155/2014/504808. Epub 2014 May 28. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24982885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bicarbonate-rich fluid secretion predicted by a computational model of guinea-pig pancreatic duct epithelium.J Physiol. 2017 Mar 15;595(6):1947-1972. doi: 10.1113/JP273306. Epub 2017 Feb 8. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27995646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuladze N., Lee I., Newman D., Hwang J., Boorer K., Pushkin A., et al. (1998). Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and functional expression of the human pancreatic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17689–17695 10.1074/jbc.273.28.17689 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

