The cognitive processes underlying affective decision-making predicting adolescent smoking behaviors in a longitudinal study
- PMID: 24101911
- PMCID: PMC3787307
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00685
The cognitive processes underlying affective decision-making predicting adolescent smoking behaviors in a longitudinal study
Abstract
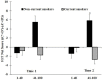
This study investigates the relationship between three different cognitive processes underlying the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) and adolescent smoking behaviors in a longitudinal study. We conducted a longitudinal study of 181 Chinese adolescents in Chengdu City, China. The participants were followed from 10th to 11th grade. When they were in the 10th grade (Time 1), we tested these adolescents' decision-making using the IGT and working memory capacity using the Self-ordered Pointing Test (SOPT). Self-report questionnaires were used to assess school academic performance and smoking behaviors. The same questionnaires were completed again at the 1-year follow-up (Time 2). The Expectancy-Valence (EV) Model was applied to distill the IGT performance into three different underlying psychological components: (i) a motivational component which indicates the subjective weight the adolescents assign to gains vs. losses; (ii) a learning-rate component which indicates the sensitivity to recent outcomes vs. past experiences; and (iii) a response component which indicates how consistent the adolescents are between learning and responding. The subjective weight to gains vs. losses at Time 1 significantly predicted current smokers and current smoking levels at Time 2, controlling for demographic variables and baseline smoking behaviors. Therefore, by decomposing the IGT into three different psychological components, we found that the motivational process of weight gain vs. losses may serve as a neuropsychological marker to predict adolescent smoking behaviors in a general youth population.
Keywords: EV model; Iowa Gambling Task (IGT); adolescents; decision-making; longitudinal study; smoking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Affective decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in 10th-grade Chinese adolescent smokers.Nicotine Tob Res. 2008 Jun;10(6):1085-97. doi: 10.1080/14622200802097530. Nicotine Tob Res. 2008. PMID: 18584472 Free PMC article.
-
Affective decision-making predictive of Chinese adolescent drinking behaviors.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2009 Jul;15(4):547-57. doi: 10.1017/S1355617709090808. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19573273 Free PMC article.
-
Affective decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in 10th grade Chinese adolescent binge drinkers.Neuropsychologia. 2008 Jan 31;46(2):714-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.09.012. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Neuropsychologia. 2008. PMID: 17996909 Free PMC article.
-
Decision-making and cognitive abilities: A review of associations between Iowa Gambling Task performance, executive functions, and intelligence.Clin Psychol Rev. 2010 Jul;30(5):562-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.04.002. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Clin Psychol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20457481 Review.
-
[Decision-making and schizophrenia].Encephale. 2011 Dec;37 Suppl 2:S110-6. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7006(11)70036-7. Encephale. 2011. PMID: 22212839 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Posttraumatic stress disorder and tobacco use: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Addict Behav. 2018 Sep;84:238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.04.024. Epub 2018 May 3. Addict Behav. 2018. PMID: 29753221 Free PMC article.
-
The somatic marker theory in the context of addiction: contributions to understanding development and maintenance.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2015 Jul 6;8:187-200. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S68695. eCollection 2015. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2015. PMID: 26185474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of Impulsivity and Risky Decision-Making with E-Cigarette-Related Outcomes Among Adolescents with Congenital Heart Disease: Variable- and Person-Oriented Approaches.Behav Med. 2025 Jan-Mar;51(1):73-84. doi: 10.1080/08964289.2024.2347226. Epub 2024 May 6. Behav Med. 2025. PMID: 38706412
-
A longitudinal analysis of adolescent decision-making with the Iowa Gambling Task.Dev Psychol. 2018 Apr;54(4):689-702. doi: 10.1037/dev0000460. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Dev Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29154644 Free PMC article.
-
THE IOWA GAMBLING TASK IN VIOLENT AND NONVIOLENT INCARCERATED MALE ADOLESCENTS.Crim Justice Behav. 2019 Nov 1;46(11):1611-1629. doi: 10.1177/0093854819847707. Epub 2019 May 12. Crim Justice Behav. 2019. PMID: 32981980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bechara A., Damasio A. R. (2005). The somatic marker hypothesis: a neural theory of economic decision. Games Econ. Behav. 52, 336–372 10.1016/j.geb.2004.06.010 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

