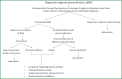
Malignant pleural effusion and algorithm management
- PMID: 24102015
- PMCID: PMC3791493
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.09.04
Malignant pleural effusion and algorithm management
Abstract
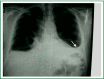
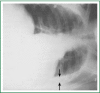
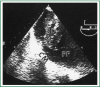
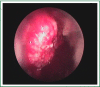
Involvement of the pleura in lung cancer is a common manifestation accompanying with reduced life expectancy. Symptoms relief and improvement of the quality of life are the primary goals of the management of malignant pleural effusion (MPE). Histological confirmation is essential for optimal patient management. Lung cancer patients, with life expectancy more than 3 months, resistant to chemotherapy should be treated with thoracentesis, intercoastal tube drainage and installation of a sclerosant agent or pleurodesis through thoracospopic procedures or placement of an indwelling pleura catheter. Talc pleurodesis (sterile asbestos-free graded, particle size >15 μm), as "poudrage" or "slurry" still remains the treatment of choice in patients with MPE resistant to chemotherapy.
Keywords: Malignant pleural effusion (MPE); pleurodesis; suicide gene therapy; thoracoscopy.
Figures

References
-
- Chernow B, Sahn SA. Carcinonomatous involvement of the pleura: an analysis of 96 patients. Am J Med 1977;63:695-702 - PubMed
-
- Sahn SA. Malignant pleural effusions. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2001;22:607-16 - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1987-2001 - PubMed
-
- Noppen M.Normal volume and cellular contents of pleural fluid. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2001;7:180-2 - PubMed
-
- Fenton KN, Richardson JD. Diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Surg 1995;170:69-74 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
