Protein kinase C isoforms at the neuromuscular junction: localization and specific roles in neurotransmission and development
- PMID: 24102585
- PMCID: PMC3867888
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12106
Protein kinase C isoforms at the neuromuscular junction: localization and specific roles in neurotransmission and development
Abstract
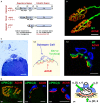
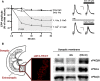
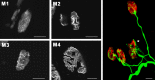
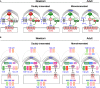
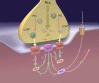
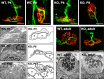
The protein kinase C family (PKC) regulates a variety of neural functions including neurotransmitter release. The selective activation of a wide range of PKC isoforms in different cells and domains is likely to contribute to the functional diversity of PKC phosphorylating activity. In this review, we describe the isoform localization, phosphorylation function, regulation and signalling of the PKC family at the neuromuscular junction. Data show the involvement of the PKC family in several important functions at the neuromuscular junction and in particular in the maturation of the synapse and the modulation of neurotransmission in the adult.
Keywords: electrical stimulation; immunofluorescence; isoforms; neuromuscular junction; neurotransmission; protein kinase C; synapse elimination.
© 2013 Anatomical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Antipenko A, Frías JA, Parra J, et al. Effect of chronic electrostimulation of rabbit skeletal muscle on calmodulin level and protein kinase activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:303–310. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:735–740. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa M, Mizoguchi A, Masutani M, et al. Ultrastructural localization of protein kinase C beta-subspecies in the axon terminal of rat neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Res. 1993;16:125–130. - PubMed
-
- Arenson MS. Muscarinic inhibition of quantal transmitter release from the magnesium-paralysed frog sartorius muscle. Neuroscience. 1989;30:827–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

